Sections of the site
Editor's Choice:
- Crimping the content of international environmental legal protection
- Kamenka (Penza region) to which federal district belongs to the city of Kamenka
- Russian principalities and land in the XII - XIII centuries
- Charles de Gaulle: Biography and Interesting Facts From the life of Charles de Gaulle Right or left
- Where does the water disappears in the kettle?
- The degree of oxidation (oxidative number, oxidation state) is H2O2 the degree of oxidation
- History of biological research
- Hydrogen Communication All Examples
- Barbaric Encyclopedia: Commod, Emperor Lucius Ely Aureli Commoda Mark Azeri Son
- History of creation and development
Advertising
| The degree of oxidation (oxidative number, oxidation state) is. The degree of oxidation (oxidative number, oxidation state) is H2O2 the degree of oxidation |
|
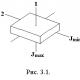
The hydrogen peroxide molecule has an angular structure (Fig. 1). Communication energy O-O (210CH / mol) is significantly less than the energy of the O-H (468 kJ / mol). Fig. 1. The structure of hydrogen peroxide molecule, indicating the valence angles between the bonds and lengths of chemical bonds. Due to the asymmetric distribution of the bonds of the H-O molecule of hydrogen peroxide is strongly polar (the dipole moment is 0.7 × 10 -29 KL × M). A strong hydrogen bond arises between hydrogen peroxide molecules, leading to their association. Therefore, under normal conditions, hydrogen peroxide is a syrup-like liquid (density - 1.44 g / cm 3), with a rather high boiling point (150.2 o C). The melting point is 0.41 o C. It has a pale blue color. Gross formula - H 2 O 2. Molar mass - 34 g / mol. Hydrogen peroxide is a good ionizing solvent. Water mixed in any relations due to the occurrence of new hydrogen bonds. The solutions are distinguished as an unstable crystalline H 2 O 2 × 2H 2 O. H2O2, the degree of oxidation of elements in itTo determine the degree of oxidation of the elements included in the hydrogen peroxide, you must first figure out for which items this value is exactly known. Hydrogen peroxide, like water, is a hydride of oxygen, and which hydrogen is known to show the degree of oxidation (+1). To find the degree of oxygen oxygen, we will take it a value for "x" and determine it using an electrophetral equation: 2 × (+1) + 2 × x \u003d 0; Therefore, the degree of oxidation of oxygen in hydrogen peroxide is equal to (-1): H +1 2 O - 1 2. Examples of solving problemsExample 1.
Example 2.
Chemical element, the degree of oxidation of which in the highest oxide is +7, corresponds to the diagram of the distribution of electrons by layers A3. Electronic scheme + X (2, 8, 5) Belongs to the atom of the chemical element: a) phosphorus b) silicon c) aluminum d) potassium A4. Electronic formula 1 s22. s22. p3. belongs to the atom: a) aluminum b) nitrogen c) calcium d) sodium A3. The characteristic of isotopes includes expression: 1) Atoms have a different atomic mass and a different charge of the nucleus 2) the number of protons in the nuclei of atoms is different, the mass of atoms is also different 3) the number of protons in the nuclei of atoms is different, the mass of atoms is the same 4) the number of neutrons in atomic nuclei is different, and the number of protons A4. In a number of sodium elements - Magnesium - Aluminum 1) the number of electronic layers in atoms is increasing 2) the number of electrons in the external electronic layer increases 3) the number of protons in atomic nuclei decreases 4) decreases the degree of oxidation of elements in oxygen compounds A5. Substance whose name sodium sulfite has a formula A6. Compounds with ion type of communication are formed in the case when atoms interact 1) identical non-metals 2) with the same electronegativity 3) with sharp different electronegitability 4) different non-metals A7. The formulas of substances with a covalent polar bond are in the group 3) CH4, LSL, SO2 4) NN3, H2S, CO2 A8. The character of the oxide of the chemical element in the atom of which 3) amphoterous 4) main A9. Acid oxides are all substances in the group 3) CO2 AL2O3, FE2O3 4) Li2O, NO, FEO A10. Silicic acid can not be obtained when interacting the pair 1) Na2SiO3 and NS1 2) SiO2 and H2O 3) K2SIO3 and H2SO4 4) K2SIO3 and H3RO4 A11. Calculations can not be dissolved in water pairs of substances 3) SO3, Na2O 4) N2O3, P2O5 A12.Lakmus acquires red in aqueous solution 3) potassium hydroxide 4) sodium chloride A13. Reaction, equationine, refers to chemical reactions of substitution 1) 2N20 \u003d 2N2 + 02 2) Na2O + H2SO4 \u003d NA2SO4 + H2O 3) NAON + NS1 \u003d NAc1 + H2O 4) 2N2O + 2NA \u003d 2NAON + H2 A14. The interaction between copper (II) hydroxide and nitric acid refers to reactions: 1) Replacement 2) Connections 3) Exchange 4) Redox IN 1. Mass of 1.5 mol of copper nitrate (II) SI (NOZ) 2 is equal 1) 125.3g 2) 283g 3) 189g 4) 188 AT 2. When burning 6 g of coal, carbon (IV) volume oxide formed IN 3. What mass is 3,1024 carbon dioxide molecules (carbon oxide (IV)) have 3,1024? 1) 220g 2) 22g 3) 0.22g 4) 11,2g AT 4 . Mass fraction of phosphorus in phosphorus oxide (V) 1)22% 2) 43,7% 3) 68% 4) 0,12% AT 5. From 120g of a 5% solution of sodium nitrite was evaporated with 40g water. Mass fraction of substance in the resulting solution: 1) 1,25 2) 0,05 3) 0,06 4) 0,075 B6. Establishing the iron will occur as a result of the reaction between 1) iron (III) and carbon oxide 2) Copper Sulfate (II) and Iron 3) iron (II) chloride and sodium hydroxide 4) gland and gray AT 7. With each of the substances whose formulas you12, Cu (OH) 2, Fe will be 1) zinc sulfate 2) magnesium nitrate 3) sodium hydroxide 4) sulfuric acid AT 8. Water formation is possible in the interaction of solutions of substances 3) nnose and k3ro4 4) sa (he) 2 and feves13 AT 9. In accordance with the abbreviated ionic equation Cu2 + + 2On- \u003d Cu (OH) 2, the pair of electrolytes interacts 3) SUC12 and sa (it) 2 4) con and cu2s The degree of oxidation is a charge that could occur at an atom in a molecule or ion if all its connections with other atoms were torn, and the general electronic pairs left with more electronegative elements. In which of the compounds oxygen shows a positive degree of oxidation: H2O; H2O2; CO2; Of2? OF2. This compound oxygen has a degree of oxidation + 2 Which of the substances is only a reducing agent: FE; SO3; CL2; HNO3? sulfur oxide (IV) - SO 2 What element in the III period of the periodic system D.I. Mendeleev, being in a free state, is the strongest oxidizing agent: Na; Al; S; CL2? CL chlorine V -Chest What classes of inorganic compounds include the following substances: HF, PBO2, HG2SO4, NI (OH) 2, FES, NA2CO3? Sophisticated substances. Oxides. Make formulas: a) acidic potassium salts of phosphoric acid; b) the main zinc salt of coalic acid H2CO3. What substances are obtained by interaction: a) hydraulic acids; b) acids with base; c) salts with salt; d) base with salt? Give examples of reactions. A) metal oxides, metals salts. C) salts (only in solution) D) a new salt, insoluble base and hydrogen What kind of substances listed below will react hydrochloric acid: N2O5, Zn (OH) 2, Cao, AGNO3, H3PO4, H2SO4? Make equations of possible reactions. Zn (OH) 2 + 2 HCl \u003d ZnCl + H2O Cao + 2 HCl \u003d CaCl2 + H2O Indicate how the type of oxides includes copper oxide, and prove it using chemical reactions. Metal oxide. Copper oxide (II) Cuo - black crystals crystallized in monoclinic syngony, density 6.51 g / cm3, melting point 1447 ° C (under oxygen pressure). When heated to 1100 ° C is decomposed with the formation of copper oxide (I): 4CUO \u003d 2CU2O + O2. It does not dissolve in water and does not respond to it. It has low-voltage amphoteric properties with the predominance of the main. In aqueous solutions, ammonia forms Tetraammondi hydroxide (II): Cuo + 4NH3 + H2O \u003d (OH) 2. Easily reacts with diluted acids with the formation of salt and water: Cuo + H2SO4 \u003d CUSO4 + H2O. When spraying with alkalis, Cuprats forms: Cuo + 2KOH \u003d K2CUO2 + H2O. It is reduced by hydrogen carbon monoxide and active metals to metal copper: Cuo + H2 \u003d Cu + H2O; Cuo + Co \u003d Cu + CO2; Cuo + Mg \u003d Cu + Mgo. It turns out when calculating the hydroxide of copper (II) at 200 ° C: Cu (OH) 2 \u003d Cuo + H2 Oxide and copper hydroxide (II) or when oxidizing metal copper in air at 400-500 ° C: 2CU + O2 \u003d 2CUO. 6. Finish the reaction equations: Mg (OH) 2 + H2SO4 \u003d MgSO4 + 2H2O NaOH + H3RO4 \u003d NaH2PO4 + H2O PE \u003d 1 percentage concentration - a mass of a substance in grams contained in 100 grams of the solution. If 100 g of solution contains 5 g of salts, how much should it be for 500 g? the titer is a mass of substances in grams contained in 1 ml of solution. 0.3 g enough for 300 ml. SA (OH) 2 + H2CO3 \u003d SAO + H2O 2 / Characteristic reaction - the neutralization reaction Ca / O / 2 + H2CO3 \u003d SASO3 + H2O 3 / react with acid acid oxides / 2 + CO2 \u003d SAS3 + H2O 4 / with sour Saluing SA / 2 + 2KNSO3 \u003d K2CO3 + SASO3 + 2N2O 5 / Alkali join the metabolic reaction with salts. If the sediment 2NAOH + CUCL2 \u003d 2NACL + CU / OH / 2 / SEEDS / 6 / Solutions alkalis are reacting with non-metals. Also with aluminum or zinc. OSR. Name the three methods of producing salts. Answer Confirm the reaction equations A) Neutralization reaction.. After evaporation of water, the crystal salt is obtained. For example: B) Acid oxide reaction (See paragraph 8.2). It is also a variant of the neutralization reaction: IN) Acid reactions with salts. This method is suitable, for example, in the event that an insoluble salt is formed, precipitated: Which of the following substances can react among themselves: NaOH, H3PO4, AL (OH) 3, SO3, H2O, CAO? Answer Confirm the reaction equations 2 NaOH + H3PO4 \u003d Na2HPO4 + 2H2O Cao + H2O \u003d CA (OH) 2 Al (OH) 3 + NaOH \u003d Na (Al (OH) 4) or Naalo2 + H2O SO3 + H2O \u003d H2SO4 VI-part The core of the atom (protons, neutrons). Atom is the smallest particle of the chemical element, which preserves all its chemical properties. The atom consists of a kernel having a positive electrical charge, and negatively charged electrons. The charge of the core of any chemical element is equal to the product Z on E, where Z is the sequence number of this element in the periodic system of chemical elements, E is the magnitude of the elementary electric charge. Protons - Stable elementary particles having a single positive electrical charge and mass, in 1836 times greater than the mass of the electron. The proton is the kernel of the atom of the easiest element - hydrogen. The number of protons in the kernel is Z. Neutron - neutral (non-electrical charge) elementary particle with a mass, very close to the mass of the proton. Since the mass of the nucleus is made from the mass of protons and neutrons, the number of neutrons in the atom kernel is equal to z, where a is a mass number of this isotope (see a periodic system of chemical elements). Proton and neutron included in the kernel are called nucleons. In the nucleus, nucleons are connected by special nuclear forces. Electrons Electron - The smallest particle of a substance with a negative electric charge E \u003d 1.6 · 10 -19 Coulomb adopted for an elementary electrical charge. Electrons, rotating around the core, are located on electronic shells K, L, M, etc. K - the shell closest to the kernel. The size of the atom is determined by the size of its electronic shell. Isotopes Isotope - atom of the same chemical element whose core has the same number of protons (positively charged particles), but a different number of neutrons, and the element itself has the same atomic number as the main element. By virtue of this, the isotopes have various atomic masses. the conditional charge of the atom in the molecule calculated according to the assumption that the molecule consists only of ions. To determine the degree of oxidation of atoms in chemical compounds, followed by the following rules: 1. Oxygen In the chemical compounds always attribute the degree of oxidation -2 (the exception is oxygen fluoride of 2 and peroxides of type H 2 O 2,where oxygen has a degree of oxidation, respectively, +2 and -1). 2. The degree of oxidation hydrogen In compounds, they consider equal to +1 (exception: 3.
Metals in all connections have positive values 4. The degree of oxidation of neutral molecules and atoms (for example, H 2, C, etc.) is zero, as well as metals in free state. 5. For elements that are part of complex substances, the degree of oxidation 2 (+1) + x + 4 (-2) \u003d 0, 6 = 0, x \u003d 6. Reactions, resulting in which the degree of oxidation of the elements is called, are called redox. The main provisions of the theory of the OSR 1) Oxidationcall the process return electrons atom, molecule or 2) Restorationcall the process attachment electrons atom, S + 2E \u003d S -2. 3) atoms, molecules or ions, sending electrons called reducing agents.Atoms, molecules or ions, attaching electronscalled oxidifiers. 4) Oxidationalways accompanied restorationand vice versa, restorationalways connected by S. oxidationwhat can be expressed by the equations: reducing agent - E↔Okoslitel; Oxidizer + E↔Vector. Redox reactions are the unity of two opposing processes - oxidation and recovery. Oxidation and recovery processes express electronic equations.They include a change in the degree of oxidation of atoms and the number of electrons given by the reducing agent and the oxidizing agent adopted. So, for reaction 2k +1 i -1 + 2fe +3 Cl 3 -1 \u003dI 2 0 + 2fe +2 Cl 2 -1 + 2k +1 Cl -1electronic equations are viewed 2i -1 - 2e\u003d I 2 0 oxidation process (reducing agent); Fe +3 + E= Fe +2.recovery process (oxidizer). For the compilation of equations of redox reactions, two methods are used: the electronic balance method and the ion-electronic method (half-formation method). Electronic Balance Methodis universal. In this method compare the degrees of oxidation of atoms in the initial and finite substances, guided by the rule: the number of electrons given by the reducing agent should be equal to the number of electrons connected by the oxidant.To compile the equation, you need to know the formulas of the reacting substances and reaction products. The latter are defined either experienced way, or on the basis of the known properties of elements. Ion-electronic method (half-formation method)uses representations about electrolytic dissociation.The method is used only in the preparation of the OSR equations occurring in solution.In contrast to the electronic balance method, this method gives a more correct idea of \u200b\u200bthe oxidation processes - reduction in solutions, since it considers ions and molecules in the form in which they exist in the solution. Weak electrolytes or low-soluble substances are recorded in the form of molecules, and strong - in the form of ions. At the same time, take into account that in water ions can participate in the reaction H +,He - and molecules H 2 O.Rules for finding coefficients in the OSR equations flowing into acidic, alkaline and neutral media, unequal. If the reaction is medium sour Rule. Each binds to two hydrogen ions with the formation of one water molecule: [O -2] + 2N + \u003d H 2 O. Each it takes from the water molecule, while two hydrogen ions are released: H 2 O - [O -2] \u003d 2N +. If the reaction is medium alkaline Rule. Each released oxygen particlereacts with one water molecule, forming two hydroxide ions: [o -2] + H 2 O \u003d 2H. Each missing oxygen particleit is taken from two hydroxide ions to form one water molecule: 2H - - - [O -2] \u003d H 2 O. If the reaction is medium neutral Rule. Each released oxygen particleit interacts with one water molecule, forming two hydroxide ions: [o -2] + H 2 O \u003d 2H. Each missing oxygen particleit is taken from the water molecule to form two hydrogen ions: H 2 O - [O -2] \u003d 2N +. The selection of ORP coefficients by ion-electronic method is carried out in several stages: 1) Write a reaction scheme (reaction of an acidic acid) in molecular form, KMNO 4 + Na 2 SO 3 + H 2 SO 4 \u003d MNSO 4 + Na 2 SO 4 + K 2 SO 4 + H 2 O; 2) Write a reaction scheme in ion form and identify ions and molecules that change the degree of oxidation: K + + MPO 4 - + 2NA + + SO 3 2- + 2H + + SO 4 2- \u003d Mn 2+ + SO 4 2- + 2NA + + SO 4 2- + 2k + + SO 4 2- + H 2 O; 3) make ion-electronic equations with the participation of dedicated ions For this reaction: Lack of oxygen atoms in an acidic environment takes out of the water molecule: SO 3 2- + H 2 O - 2e - \u003d SO 4 2- + 2N +; Excess oxygen atoms in an acidic environment
binds to hydrogen ions in MNO 4 - + 8H + + 5E - \u003d Mn 2+ + 4N 2 o; 4) multiply the obtained equations for the smallest factors for the balance of electrons: SO 3 2- + H 2 O - 2E - \u003d SO 4 2- + 2H + | 5 MPO 4 - + 8H + + 5e - \u003d Mn 2+ + 4H 2 O | 2. 5SO 3 2- + 5H 2 O - L0E - \u003d 5SO 4 2- + 10H + 2MNO 4 - + 16H + + 10E - = 2mn 2+ + 8H 2 O; 5) summarize the obtained electron-ion equations: 5SO 3 2- + 5N 2 O - 10E - + 2MNO 4 - + 16H + + 10E - \u003d 5SO 4 2- + 10H + + 2MN 2+ + 8H 2 O; 6) reduce such members and get an ion-molecular equation 5SO 3 2- + 2MPO 4 - + 6N + \u003d 5SO 4 2- + 2MN 2+ + 3N 2 O; 7) at the obtained ion-molecular equation to make a molecular reaction equation: 2kmno 4 + 5NA 2 SO 3 + 3H 2 SO 4 \u003d 2MNSO 4 + 5NA 2 SO 4 + K 2 SO 4 + 3H 2 O. Redox reactions are separated into three types: 1) intermolecular -these are reactions in which the oxidizing agent and the reducing agent are in different substances: 2N 2 8 +6 O 4 (conc.) + Cu 0 \u003d Cu +2 SO 4 + S +4 O 2 + 2N 2 O. 2) intramolecular -these are reactions in which the oxidizing agent and the reducing agent are in the same molecule (atoms of different elements): 2x1 +5 o 3 -2 \u003d 2xl -1 + 3o 2 ° 3) Disproportionation (self-examination reaction) Peroxide, or hydrogen peroxide- Oxygen compound of hydrogen (peroxide). Formula: H2O2 Physical Properties:hydrogen peroxide is a colorless syrupy liquid, the density - 1.45 g / cm3 changes to the number of very weak, since dissociates in a very low degree: according to I steps I: by stage II: Chemical properties:in the interaction of a concentrated solution H2O2 S.metal hydroxides are formed by their peroxides: Na2O2, CaO, MGO2 IDR. Peroxides, or peroxide- These are salts of H2O2, consisting of positively charged ions of metals and negatively charged O22- ions, the electronic structure of their anion as follows: H2O2 shows redox properties: oxidizes the substance standard electronic potential (E °) does not exceed 1.776 V; Restores substances in which E ° is greater than 0.682 V. Oxidative and reducing properties H2O2they are explained by the fact that the degree of oxidation -1 in oxygen atoms has an intermediate value between the degrees of oxidation -2 and 0. Oxidative properties are more characteristic. H2O2 here serves as an oxidizing agent.  In these cases, hydrogen peroxide is a reducing agent. Salts H2O2 -peroxides (peroxide) also possess redox properties: Here Na2O2 is a reducing agent. Getting:the H2O2 industry is obtained by the interaction of diluted with sulfuric acid with barium peroxide WAO2: H2SO4 (spz.) + WAO2 \u003d VASO4 + H2O2, and the concentrated hydrogen peroxide is obtained by distillers in vacuo. Pergedol- 30% aqueous H2O2 solution. The oxidative capacity and safety of hydrogen peroxide gave the possibility of widespread use in many sectors of the national economy: in industry - for whitening fabrics, fur; in the food industry - for canning products; In agriculture - for the drying of seeds, in the production of a number of organic compounds, for example, in the production of glycerol: an intermediate product when obtaining glycerol - allyl alcohol CH2 \u003d CH - CH2Os oxidize with H2O in glycerin s3n5 (he) 3, Used in rocket technology as a strong oxidizing agent. The 3% H2O2 is used in pharmaceutical for medical purposes as a disinfectant. |
New
- Theorem on the change in the number of mechanical system of the theorem change the amount of system movement
- Tag: functions of several variables Geometric meaning of the differential of two variables
- Theorem on the change in the number of movement of the dynamics of the theorem on the change in the amount of movement
- Changing the amount of mechanical system of the dynamics of the theorem on the change in the amount of movement
- Speed \u200b\u200bof free fall
- How to calculate the limits of functions without using differential calculus
- How to find a gradient function
- Distance from point to point: Formulas, examples, solutions
- Solution of all types of limits with a detailed decision
- Cross-section inertia moments