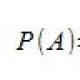Sections of the site
Editor's Choice:
- Sunday School Graduation (Toosh) Sunday School Graduation Certificate
- Holy doctor-martyr eugene botkin
- Passion-bearer Evgeny Botkin
- How to get rid of anxiety, fear and worry
- What is the "Napoleon complex" Napoleon syndrome in men psychology
- Evgeny botkin
- Female voice: classification, lowest and highest female voice
- How does life change after the experience of enlightenment (awakening)?
- The main points of testing
- How to get rid of the fear of death: advice and psychotherapeutic help
Advertising
| 10 largest emergencies in the world. The most terrible man-made disasters. Impact assessment and conclusions |
|
Man-made disasters often occur as a consequence of natural disasters, but also because of worn-out equipment, greed or carelessness. The memory of them serves as an important lesson for humanity, because natural disasters can harm us, but not the planet, but man-made ones pose a threat to absolutely the entire surrounding world. Oil train wreck at Lak-Megantic, July 6, 2013. The disaster took place in the east of the Canadian province of Quebec. A train carrying seventy crude oil tanks derailed and the tanks exploded. More than half of the buildings in the city center were destroyed by the explosion and subsequent fire, killing about fifty people. An explosion at the Phillips Petroleum Company chemical plant, October 23, 1989, in Pasadena, Texas. Due to an oversight of employees, a large leak of combustible gas occurred, and a powerful explosion occurred, equivalent to two and a half tons of dynamite. It took firefighters over ten hours to put out the flames. 23 people were killed, another 314 were injured. An explosion in a coal mine in Centralia, Illinois on March 25, 1947. The town, now better known for the eternal underground fire, which served as the prototype of the fire in the game and the movie "Silent Hill", suffered in the middle of the XX century. It was then that at a local mine, an explosion of coal dust buried more than a hundred people - some instantly died under the rubble, others from poisonous smoke. Explosion in Halifax, December 6, 1917. In the bay of the Canadian year Halifax, the French warship Mont Blanc heading for France collided with the Norwegian ship Imo. The problem was that Mont Blanc was filled to the brim with explosives, and the force of the explosion was enough to destroy half the city. Two thousand people died, nine thousand were injured. Bhopal disaster, December 3, 1984 One of the largest man-made disasters in history that occurred in the Indian city of Bhopal. As a result of an accident at a chemical plant that produces pesticides, a toxic substance, methyl isocyanite, was released. On the day of the release, about 3 thousand people died, another 15 thousand - in subsequent years, and in one way or another, hundreds of thousands were affected. The collapse of a building in the Bangladeshi city of Savar, April 24, 2013. The Rana Plaza shopping mall, which also housed clothing businesses, collapsed during rush hour due to non-compliance with safety precautions during construction. 1127 people died, another 2500 were injured. Explosion at a chemical plant in Oppau, Germany, September 21, 1921. At the plant where the disaster happened, an explosion had already thundered a month before that killed a hundred people. But measures were not taken, and the next accident claimed the lives of 600 employees and bystanders, injuring several thousand. 12 tons of a mixture of sulfate and ammonium nitrate exploded with a force of 5 kilotons of TNT, literally wiping the town off the face of the earth. Chernobyl accident, April 26, 1986. The largest accident in the history of nuclear energy, which has become a kind of symbol of man-made disasters. Reactor explosion on Chernobyl nuclear power plant threw out radioactive substances into the atmosphere, because of which several settlements had to be evacuated. Only 31 people died, but hundreds and thousands of people suffered from the effects of radiation, and huge areas on the territory of Ukraine and Belarus became uninhabitable for many years. When talking about man-made disasters, they mean oil spills, nuclear disasters, major incidents at factories. All of them had consequences for the local population and for environment. Nuclear and atomic disastersNuclear energy remains the most dangerous in disasters and disasters. Accidents at such facilities are rated on a seven-point scale.Chernobyl disaster (Ukraine)The largest disaster to date is considered the disaster at the Chernobyl nuclear power plant, which occurred in 1986. During the explosion at the station, the fourth reactor was completely destroyed. The fire lasted for two weeks and could not be extinguished.Radioactive substances thrown into the air led to the death of 56 thousand people. The most infected were Belarus, western Russia and northern Ukraine. Fukushima (Japan)The most recent terrible atomic disaster is recognized as the accident that occurred in 2011 in Japan at the Fukushima nuclear power plant. This happened after a nine-point earthquake. The disaster caused the death of more than 25 thousand people. But its main consequence is a global radiation threat associated with damage to the reactor at a nuclear power plant. Three Mile Island NPP (USA)In the history of America, the accident in the state of Pennsylvania in 1979 is considered the worst accident. It happened at the Three Mile Island nuclear power plant. Due to the inoperative cooling system, some elements of the reactor partially melted. The largest emergency situations at enterprisesThe terrible incidents that have gone down in history also occurred at enterprises, which we will tell you about in more detail.Chemical plant "Mayak" (Chelyabinsk-40, Russia)In 1959, a serious man-made accident occurred at a chemical plant in the closed city of Chelyabinsk-40, which was declassified only after 1999. The explosion raised radioactive substances to a height of up to 2 kilometers, which settled, contaminating an area equal to 23 thousand square meters. km. Medical Clinic (Goiania, Brazil)The tragedy happened in 1987. The medical clinic in the Brazilian city of Goiânia was no longer operational. From this abandoned clinic, several people stole a container containing radioactive powder. The owner of the landfill, who bought this container from the looters, demonstrated the glowing powder in it to his friends. The area near the city turned out to be infected, and it will be possible to live on it again only after 300 years. Largest oil spillsMore than a hundred states faced the problem of an oil spill, which had significant environmental impact comparable to nuclear explosions.Explosion of an oil platform (Gulf of Mexico)The Deepwater Horizon oil drilling platform became known to the whole world in 2010 after an explosion occurred on it, as a result of which crude oil flowed into the waters of the Gulf of Mexico for three and a half months. Thus, 670 thousand tons of oil got into the water.Wreck of a bulk tanker (coast of Brittany)In 1978, off the coast of Brittany, there was a massive oil spill that resulted in the wreck of the tanker Amoco Cadiz. 23 thousand of crude oil spilled into the sea. The French seashore was polluted for two hundred miles. Due to the conduct of hostilities, they began to fight the consequences of this disaster late: 600 km of the coasts were already polluted. A thousand square kilometers of the bay's surface was covered with oil. The worst man-made disaster in the history of mankindThe most terrible man-made disaster in history is considered an explosion at a chemical plant in the Indian city of Bhopal. The tragedy took place in early December 1984. About 20 thousand people died as a result of the disaster, and up to 600 thousand were injured. The water and territory of the city and its surroundings remain contaminated to this day. There were other terrible events in history, but not everyone is to blame. Sometimes tremendous destruction and mass casualties occurred at the behest of nature. The site has an article about the most terrible events of the XX century. An emergency situation is the result of the impact of a natural or man-made disaster that caused people and damage to the environment. Emergency statistics allows you to track the consequences, develop measures to counter such events and evaluate the effectiveness of the measures taken. The main causes of emergencies are the impact on nature and conflicts of a political, military, social nature. Classification of incidentsThe Government Decree of May 21, 2007 No. 304 introduced the classification of emergencies. Parameters of the spread of natural and man-made accidents: Biological and social catastrophesTechnogenic accidentsTypes of man-made disasters:
Technogenic disasters are fraught with the release of biological, chemical and radioactive substances and the outbreak of fires at power plants or transport. Statistics of technogenic emergencies by years:
Emergency statistics for 10 years contains many examples of large-scale incidents. This includes:
According to the operational forecast of the Ministry of Emergency Situations of the Russian Federation in October 2018, there was a risk of emergency situations in maritime transport in the waters of the Sea of Okhotsk and the Sea of Japan. Emergencies by regionEmergency statistics for 2017 includes 177 incidents. Distribution of events by constituent entities of the Russian Federation:
Total from emergencies 36483 people suffered. Most of falls on the inhabitants of the Primorsky (16912) and Altai (4154) regions, as well as the Republic of Adygea (6715). As a result of emergency accidents, 556 people died. Most of it falls on the Krasnodar Territory (51), Saratov region(31), the Republic of Dagestan (30) and Tatarstan (25). And also to the Stavropol (23) and Trans-Baikal Territories (20). Emergency statistics in Russia for 2017 allows us to call the year a relatively “calm” one. The number of emergencies has decreased by 41%. The number of victims decreased by 73%, the number of deaths by 30%. According to the Ministry of Emergency Situations, the emergency statistics show a positive trend. Prevention and elimination of incidentsThe Russian Emergency Prevention System (RSChS) was created by Government Decree No. 261 of 18.04.1992. Its activities are regulated by this and other regulatory documents. The key task of the structure is timely response to all kinds of incidents and emergency response in Russia. The leading role is assigned to the units of the Ministry of Emergency Situations of the Russian Federation. Coordination of actions to protect against emergencies is carried out by:
Each organization must develop an emergency plan. The document must contain a list of mandatory actions in the event of an emergency. Newly hired employees must undergo an introductory briefing on civil defense and emergency situations. Emergencies in other countriesEmergency statistics show that every year from different kinds natural disasters about 50 thousand people die in the world. Types of natural emergencies:
Between 1960 and 2015, the number of disasters tripled. The main reason is atmospheric-hydrospheric phenomena. The statistics of man-made emergencies record no less destructive consequences - the death of people, damage to the environment. Among natural disasters 2018 was the largest earthquake in Indonesia, followed by a flood. Emergency statistics have about 1550 dead. Another 152 thousand citizens are under the rubble of destroyed houses.
ConclusionWe live in disaster. Emergencies are comparable to wars in terms of the scale of their consequences. In the 21st century, they claimed hundreds of thousands of human lives, left behind millions of victims, destruction and damage that is often irreparable. Only competent actions in emergency situations can save human lives. Billions of dollars are spent annually to deal with the consequences of emergencies. In Russia alone, losses annually reach 60 billion rubles. On April 26, the world remembers one of the largest man-made disasters of the 20th century - the explosion at the Chernobyl nuclear power plant. FBA "Economics Today" prepared an overview of the most famous disasters of the last century. Why do disasters happen? Most often this is an absurd coincidence of a series of events and the notorious human factor. Halifax December 6, 1917. 3000 tons explosives in the hold of the French military transport "Mont Blanc", which entered the Canadian port of Halifax, became the cause of the most powerful man-made disaster of the early 20th century. The explosion exposed the bottom of the bay, and the ship's parts were scattered within a radius of 20 kilometers. More than 3,000 people died, 2,000 were missing, and about 9,000 were injured. The city was engulfed in fires and covered with rubble. The next day, frosts hit here, a storm began, and a day later a storm hit Halifax. The cause of the accident is the human factor: the captain of the ship carrying dangerous cargo made a mistake while maneuvering and collided with another ship. "Lighthouse" September 29, 1957. The closed city of Chelyabinsk-40 (now Ozersk). The strongest explosion at the Mayak enterprise, which was engaged in the production of weapons-grade plutonium. Due to the failure of the cooling system, about 20 million curies of radioactive substances were released into the atmosphere (for comparison: during Chernobyl accident- 50 million curies). A cloud of radioactive substances covered an area of 23,000 km² with a population of 270,000 people in 217 settlements in three regions: Chelyabinsk, Sverdlovsk and Tyumen. The victims of this accident were about 160 thousand people who received a large dose of radiation. The reason - errors in the operation of the waste storage. Bhopal Chemical Plant Union Carbide December 3, 1984 Accident at a large chemical plant that produced insect pest control products in the Indian city of Bhopal. In one hour, as a result of a lethal gas leak, more than 500,000 people were poisoned. About 4,000 people died on the day of the accident, 8,000 within two weeks. Grass turned yellow in the area, foliage fell from trees, animals died en masse. More than 16,000 died later. local residents... Thousands have lost their sight. The accident was named - chemical Hiroshima. The consequences of the disaster are still being felt. The exact cause of the accident has not been established. However, there is an assumption that this was a gross violation of safety regulations and deliberate sabotage of the enterprise. Chernobyl April 26, 1986. Explosion at the fourth reactor. More than one hundred tons of burning uranium was released into the atmosphere. More than 135 thousand people were evacuated from a 30-kilometer zone around the station. Thousands of people were involved in eliminating the consequences of the accident. The radiation level was such that the microcircuits of the robots extinguishing the fire were failing! Many liquidators died within a few days. The radioactive cloud covered not only many regions of the USSR, but also spread over a number of European countries. Work to eliminate the consequences of this accident was not completed even 30 years after the tragedy. The cause of the accident is the human factor. The cost of the disaster is $ 200 billion. Piper alpha July 6, 1988. Explosion on the Piper Alpha oil platform. The victims of the accident were 167 personnel and 226 employees. Only 59 managed to survive in this hell. The explosion was provoked by a gas leak, and the ill-considered and indecisive actions of the personnel only exacerbated the situation. The pipelines of the Piper Alpha platform were connected to a common network with other platforms that continued to operate and pump oil and gas. And for a very long time this work was not stopped, which only fed the fire. The cost of the accident is $ 3.4 billion. Chemical plant AZF (Toulouse, France) September 21, 2001. Exploded 300 tons of ammonium nitrate, which were in the warehouse of finished products. This resulted in the death of 30 people, injuries of 3.5 thousand. Thousands of residential buildings were also destroyed and damaged, more than 300 educational institutions... 40 thousand people were left without a roof over their heads. The reason is non-observance of safety rules for storing explosive substances. The price is 3 billion euros. NPP "Fukushima-1" March 11, 2011. The strongest earthquake in Japan (tremors reached a magnitude of 9) triggered a huge tsunami wave that splashed out onto the northeast coast and damaged 4 of the 6 reactors of the nuclear power plant. Then the cooling system was disabled, there were several explosions. Iodine-131 and cesium-137 were thrown into the air. Their amount was 20% of the emissions after the accident at the Chernobyl nuclear power plant. It will take about 40 years to eliminate the accident. The cost of the disaster is $ 74 billion. Sometimes it is quite difficult to assess the scale of a particular world catastrophe, because the consequences of some of them can manifest themselves many years after the incident itself. In this article, we will present 13 of the most terrible disasters the world. Among them are accidents that occurred on the water, in the air, and on the ground, through the fault of man and for reasons beyond his control, widely known and those that are not known to a very large circle of people. Wreck of the superliner "Titanic"Date Time: 14.04.1912 - 15.04.1912 Primary victims: at least 1.5 thousand people Secondary victims: unknown The British superliner "Titanic", which was called "the most luxurious ship" of its time and "unsinkable", gained worldwide fame. Unfortunately - sad. On the night of April 14-15, during its maiden voyage, the superliner collided with an iceberg and sank after more than two hours. The disaster was accompanied by numerous casualties among passengers and crew. On April 10, 1912, the liner embarked on its last voyage from the port of Southampton to American New York, having on board almost 2.5 thousand people - passengers and crew. One of the reasons for the disaster was that there was a tense ice situation on the liner's route, but the captain of the Titanic Edward Smith for some reason did not attach any importance to this even after receiving numerous warnings about floating icebergs from other ships. The liner was moving almost at its maximum speed (21-22 knots); There is a version that Smith fulfilled the unofficial requirement of the White Star Line, which owned the Titanic, to receive the Blue Ribbon of the Atlantic on the very first voyage, the prize for the fastest crossing of the ocean. Late at night on April 14, the superliner collided with an iceberg. A block of ice, which the lookout did not notice in time, proportioned the five bow compartments of the ship on the starboard side, which began to fill with water. The problem turned out to be that the designers did not count on the occurrence of a 90-meter hole in the ship, and here the whole survivability system was powerless. In addition, the "super-safe" and "unsinkable" ship did not have a sufficient number of lifeboats, and those that were, for the most part, turned out to be irrationally used (12-20 people sailed on the first boats, 65 -80 with a capacity of 60 people). The result of the disaster was the death, according to various sources, from 1496 to 1522 passengers and crew members. Today the remains of the "Titanic" rest at a depth of about 3.5 km in the Atlantic. The hull of the ship gradually collapses and finally disappears at the turn of the XXI and XXII centuries. The explosion of the 4th power unit of the Chernobyl nuclear power plantDate Time: 26.04.1986 Primary victims: 31 people from the ChNPP-4 duty shift and fire brigades who arrived to extinguish the fire Secondary victims: 124 people suffered from acute radiation sickness, but survived; up to 4 thousand liquidators, died within 10 years after liquidation; from 600,000 to a million suffered from the elimination of the consequences of radioactive contamination and stay in contaminated areas or along the movement of a radioactive cloud The accident at the Chernobyl nuclear power plant is a man-made disaster on the territory of Ukraine, between the cities of Pripyat and Chernobyl. As a result of the explosion of the 4th power unit of the Chernobyl nuclear power plant, a large amount of radioactive substances were released into the atmosphere, which led to the contamination of the surrounding territories and the formation of a radioactive cloud that swept through the territory of the USSR, Europe and reached the United States. The accident occurred due to several factors - haste on the part of the ChNPP management, insufficient competence of the ChNPP-4 duty shift, errors in the design and construction of the RBMK-1000 reactor and the NPP unit itself. On the morning of April 26, tests of the reactor were planned at ChNPP-4, which were supposed to demonstrate the possibility of operation of the reactor cooling system in the interval between the shutdown of the reactor and the launch of emergency diesel generators. However, due to some factors, the test was postponed to the night of April 26-27, which is why it was carried out by an unprepared and not forewarned change, and xenon gas accumulated in the reactor after 10 hours of idling. All this together led to the fact that when the reactor was artificially shut down, its power first fell below the critical level, and then began to grow like an avalanche. Attempts to activate AZ-5 (emergency protection) instead of eliminating the emergency situation worked as an additional catalyst for increasing the temperature of the reactor, and as a result, a powerful explosion occurred. Only one person died directly in the explosion, another one died a few hours later from his injuries. The rest of the victims received shock doses of radiation in the process of extinguishing the fire and initial liquidation of the consequences, due to which another 29 people died during the following months of 1986. The population of the first 10-kilometer and then 30-kilometer zone around the Chernobyl nuclear power plant was resettled. The resettled people were told that they would come back in three days. However, in fact, no one came back. The liquidation of the consequences of the explosion at the Chernobyl nuclear power plant took more than a year, cost billions of rubles, 240 thousand people passed through the ChEZ in 1986-1987. The city of Pripyat was completely abandoned, hundreds of villages and villages were razed, Chernobyl-4 is now a partially inhabited city - the military, police and employees of the remaining three blocks of the Chernobyl nuclear power plant live there. Terrorist act 9/11Date Time: 11.09.2001 Primary victims: 19 terrorists, 2977 police, military, firefighters, medics and civilians Secondary victims: 24 people are missing, the exact number of injured is unknown The terrorist attacks of September 11, 2001 (better known as 9/11) are the largest terrorist attack in American history. A series of four coordinated terrorist attacks claimed nearly 3,000 lives and wreaked havoc on the buildings attacked. According to the official version of events, on the morning of September 11, four groups of a total of 19 terrorists, armed only with plastic knives, hijacked four passenger airliners, sending them to targets - the World Trade Center towers in New York, the Pentagon and the White House (or Capitol) in Washington. The first three planes hit objects, what happened on board the fourth is not known for certain - according to the official version, the passengers entered into a fight with the terrorists, because of which the plane crashed in Pennsylvania, without reaching its target. Of the more than 16 thousand people who were in both towers of the WTC, at least 1,966 people died - mainly those who were in the places of attack of aircraft and on floors above, as well as at the time of the collapse of the towers, they were helping the injured and carrying out the evacuation. 125 people died in the Pentagon building. All 246 passengers and crew members of the hijacked aircraft were also killed, along with 19 terrorists. In the process of eliminating the consequences of the terrorist attack, 341 firefighters, 2 paramedics, 60 police officers and 8 ambulance workers were killed. The total death toll in New York alone was 2,606. The 9/11 terrorist act became a real tragedy in the United States, citizens of another 91 states were also killed. The terrorist attack provoked the US invasion of Afghanistan, Iraq, and later in Syria under the banner of the fight against terrorism. Disputes about the true reasons for the terrorist attack and the course of events on this tragic day have not subsided until now. Fukushima-1 accidentDate Time: 11.03.2011 Primary victims: 1 person died from the consequences of radiation contamination, about 50 people died during the evacuation Secondary victims: up to 150,000 people were evacuated from the zone of radioactive contamination, more than 1,000 of them died within a year after the disaster The catastrophe that occurred on March 11, 2011, simultaneously combines the features of man-made and natural disasters. A violent magnitude nine earthquake, followed by a tsunami, caused a power failure at the Daiichi nuclear plant, shutting down the cooling of the nuclear fueled reactors. In addition to the monstrous destruction that was caused by the earthquake and tsunami, this incident led to serious radioactive contamination of the territory and water area. In addition, the Japanese authorities had to evacuate up to one hundred and fifty thousand people due to the high likelihood of serious illness due to exposure to severe radiation. The combination of all these consequences gives the Fukushima accident the right to be called one of the worst disasters in the world in the twenty-first century. The total damage from the accident is estimated at $ 100 billion. This amount includes the costs of liquidation of consequences and payment of compensation. But at the same time, we must not forget that work to eliminate the consequences of the disaster continues to this day, which accordingly increases this amount. In 2013, the Fukushima nuclear power plant was officially closed, and on its territory only work is being carried out to eliminate the consequences of the accident. Experts believe that it will take at least forty years to put the building and the contaminated area in order. The consequences of the Fukushima accident are a reassessment of safety measures in the nuclear power industry, a fall in the cost of natural uranium, and, accordingly, a decrease in the prices of shares of uranium mining companies. Collision at Los Rodeos AirportDate Time: 27.03.1977 Primary victims: 583 people - passengers and crew of both airliners Secondary victims: unknown Perhaps the biggest plane crash in the world was the collision of two planes in the Canary Islands (Tenerife) in 1977. At Los Rodeos airport, two Boeing 747 airliners owned by KLM and Pan American collided on the runway. As a result, 583 of 644 people died, including both passengers and crews of airliners. One of the main reasons for this situation was the terrorist attack at Las Palmas airport, which was staged by terrorists from the MPAIAC (Movimiento por la Autodeterminación e Independencia del Archipiélago Canario) organization. The terrorist attack itself did not entail any casualties, but the airport administration closed the airport and stopped accepting planes for fear of repeated incidents. Because of this, Los Rodeos was overwhelmed, as planes were sent to Las Palmas, in particular two Boeing 747 flights PA1736 and KL4805. At the same time, it should be noted that the plane, owned by Pan American, had sufficient fuel to land at another airport, but the pilots obeyed the controller's order. The cause of the collision itself was fog, which seriously limited visibility, as well as difficulties in negotiations between controllers and pilots, which were caused by the strong emphasis of the controllers, and the fact that the pilots were constantly interrupting each other. Collision « Dona Paz "with a tanker « Vector"Date Time: 20.12.1987 Primary victims: up to 4386 people, of which 11 are members of the crew of the tanker "Vector" Secondary victims: unknown On December 20, 1987, the Philippines-registered passenger ferry Doña Paz collided with the oil tanker Vector, causing the largest peacetime water disaster in the world. At the time of the collision, the ferry followed its standard Manila-Katbalogan route, which it sailed twice a week. On 20 December 1987, at about 06:30, the Doña Paz sailed from Tacloban and headed for Manila. At about 22:30 the ferry passed the Tablas Strait near Marinduke, according to surviving eyewitnesses, the weather was clear, but with rough seas. The collision took place after the passengers fell asleep, the ferry collided with the tanker "Vector", which was carrying gasoline and oil products. Immediately after the collision, a massive fire broke out due to the fact that oil products spilled over the sea. A strong blow and a fire almost instantly caused panic among passengers, in addition, according to survivors, the ferry did not have the required number of life jackets. Only 26 people survived, of which 24 were passengers from Donja Paz and two from the tanker "Vector". Mass poisoning in Iraq, 1971Date Time: fall 1971 - end of March 1972 Primary victims: officially - from 459 to 6,000 deaths, unofficially - up to 100,000 deaths Secondary victims: according to various sources, up to 3 million people who could somehow suffer from poisoning At the end of 1971, a batch of grain treated with methylmercury was imported to Iraq from Mexico. Of course, the grain was not intended to be processed into food and was only to be used for planting. Unfortunately, the local population did not know Spanish, and, accordingly, all the warning labels that read "Do not eat" were not clear. Also, it should be noted that the grain was delivered to Iraq with a delay, since the planting season has already passed. All this led to the fact that in some villages, grain treated with methylmercury began to be eaten. After eating this grain, symptoms such as numbness of the limbs, loss of vision, and impaired coordination were observed. As a result of criminal negligence, according to official data, about one hundred thousand people received mercury poisoning, of which from 459 to 6 thousand died (unofficial data show other pictures - up to 3 million victims, up to 100 thousand deaths). This incident led to the fact that the World Health Organization began to monitor the circulation of grain more closely, and began to take more seriously the labeling of potentially hazardous products. Mass extermination of sparrows in ChinaDate Time: 1958-1961 Primary victims: at least 1.96 billion sparrows, no human loss known Secondary victims: 10 to 30 million Chinese starved to death in 1960-1961 Within the framework of economic policy " Great Leap Forward", In China under the leadership communist party and Mao Zedong carried out a large-scale fight against agricultural pests, among which the Chinese authorities identified the four most terrible - mosquitoes, rats, flies and sparrows. Employees of the Chinese Research Institute of Zoology calculated that due to sparrows, the volume of grain was lost during the year, with the help of which about thirty-five million people could be fed. Based on this, a plan for the extermination of these birds was developed, which was approved by Mao Zedong on March 18, 1958. All the peasants began to actively hunt birds. The most effective method was to keep them from sinking to the ground. To do this, adults and children shouted, beat in basins, brandished poles, rags, etc. This made it possible to scare the sparrows and prevent them from landing on the ground for fifteen minutes. As a result, the birds simply fell dead. After a year of hunting sparrows, the harvest has really increased. However, later, caterpillars, locusts, and other pests began to actively breed, which ate the shoots. This led to the fact that a year later, the harvest fell dramatically, and a famine ensued, which led to the death of 10 to 30 million people. Piper Alpha oil platform disasterDate Time: 06.07.1988 Primary victims: 167 people from the platform staff Secondary victims: unknown The Piper Alpha platform was built in 1975, and oil production started on it in 1976. Over time, it was converted for gas production. However, on July 6, 1988, a gas leak occurred, which led to an explosion. Due to the indecisive and ill-considered actions of the personnel, 167 people out of 226 who were on the platform died. Of course, after this event, oil and gas production on this platform was completely stopped. Insured losses amounted to approximately US $ 3.4 billion. This is one of the most famous disasters in the world associated with the oil industry. The death of the Aral SeaDate Time: 1960 - today Primary victims: unknown Secondary victims: unknown This incident is the largest environmental disaster in the territory of the former Soviet Union... The Aral Sea was once the fourth largest lake after the Caspian Sea, Lake Superior in North America, Lake Victoria in Africa. Now in its place is the Aralkum desert. Cause of disappearance The aral sea is the creation of new irrigation canals for agricultural enterprises on the territory of Turkmenistan, which took water from the Syr Darya and Amu Darya rivers. Because of this, the lake receded greatly from the coast, which led to the exposure of the bottom, covered with sea salt, pesticides and chemicals. Due to natural evaporation of the Aral Sea, over the period from 1960 to 2007, the sea lost about a thousand cubic kilometers of water. In 1989, the reservoir split into two parts, and in 2003 the volume of water was about 10% of the original. This incident resulted in serious changes in climate and landscape. In addition, of the 178 species of vertebrates that lived in the water area of the Aral Sea, only 38 remain. Explosion of the oil platform Deepwater HorizonDate Time: 20.04.2010 Primary victims: 11 people from the platform staff, 2 emergency responders Secondary victims: 17 people from the platform staff The explosion on the Deepwater Horizon oil platform that occurred on April 20, 2010 is considered one of the largest man-made disasters in the world. negative impact on the ecological situation. 11 people died directly from the explosion, and 17 were injured. Two more people died during the liquidation of the consequences of the disaster. Due to the fact that the explosion damaged pipes at a depth of 1,500 meters, about five million barrels of oil spilled into the sea in 152 days, creating a slick with an area of 75 thousand kilometers, in addition, 1770 kilometers of the coast were polluted. The oil spill threatened 400 species of animals and also led to a fishing ban. The eruption of the Mont Pele volcanoDate Time: 8.05.1902 Primary victims: from 28 to 40 thousand people Secondary victims: not known for certain On May 8, 1902, one of the most destructive volcanic eruptions in human history took place. This incident led to the emergence of a new classification of volcanic eruptions, and changed the attitude of many scientists to volcanology. The volcano awakened in April 1902, and within a month, hot vapors and gases, as well as lava, accumulated inside. A month later, a huge grayish cloud erupted at the foot of the volcano. A feature of this eruption is that the lava did not come out of the summit, but from side craters that were located on the slopes. As a result of a powerful explosion, one of the main ports of the island of Martinique, the city of Saint Pierre, was completely destroyed. The disaster claimed the lives of at least 28 thousand people. Tropical cyclone NargisDate Time: 02.05.2008 Primary victims: up to 90 thousand people Secondary victims: at least 1.5 million injured, 56 thousand missing This disaster developed as follows:
According to the UN, as a result of the riot of the elements, 1.5 million people suffered, of which 90 thousand died, and 56 thousand were missing. In addition, the major city of Yangon was severely affected, and many settlements were completely destroyed. Part of the country was left without telephone communications, internet and electricity. The streets were littered with debris, debris from buildings and trees. To eliminate the consequences of this catastrophe, the combined forces of many countries of the world and such international organizations as the UN, EU, UNESCO were needed. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Read: |
|---|
Popular:
New
- Landmarks of London in English: description and photos Characteristics for describing the object
- Addition rules
- Basic Forms of Greetings (Nihao Translation)
- Phrasal verb TURN, expressions and idioms
- BelZhD has an online scoreboard
- What is acceleration? Speed. acceleration The body is accelerated if
- Menu templates in Word: download and print
- Simple math of Bayes' theorem
- Pearson correlation criterion Correlation coefficient 1 means
- Fuzzy and random sets Basic equivalences of propositional algebra















 There have also been smaller incidents in the world. Statistics of natural emergencies and man-made accidents by country:
There have also been smaller incidents in the world. Statistics of natural emergencies and man-made accidents by country: