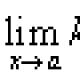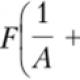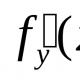Sections of the site
Editor's Choice:
- Weightless life: as astronauts sleep, eat and certify the need for the station
- "Heroic landing" allies in Normandy
- Four kingdoms of wildlife
- The main riddles of the history of Russia
- "Heroic landing" allies in Normandy (12 photos)
- Major instincts. Hunting and gathering. Three main instincts
- The brightest planet. For all and about everything
- Which planet is the brightest in the sky
- Armion Spaws and Travel
- Russian spirit!!! Great Rus !!! Nice feats of Russian warriors
Advertising
| Allied landing in Normandy value. "Heroic landing" allies in Normandy |
|
During World War II (1939-1945) from June 1944 to August 1944, the Battle of Normandy took place, which freed the allies of Western Europe from the control of Nazi Germany. The operation wore the code name "Overlord". It began on June 6, 1944, (this day was called day-d), when about 156 thousand American, British and Canadian forces landed at five beaches, stretched out 50 miles of the fortified coast of the French region of Normandy. It was one of the largest military operations in the world and demanded large-scale planning. Before the day, the Allies conducted a large-scale operation on the disinformation of the enemy, designed to mislead the Germans about the estimated invasion goal. By the end of August 1944, all Northern France was released, and by the next spring, the allies defeated the Germans. The landing in Normandy is considered the beginning of the end of the war in Europe. Preparation for the Day-DAfter the beginning of World War II, since May 1940, Germany occupied North-West France. The Americans entered the war in December 1941, and by 1942, together with the British (who were evacuated with the beaches of Dunkirk in May 1940, when the Germans cut them off during France's battle) considered the possibility of a major invasion of allies on La Mans. Next year, allies plans to cross the invasion began to increase. In November 1943, who knew about the threat of invasion of the North Coast of France, set the defensive operations in the region, although the Germans did not know exactly where the allies hit. Hitler accused Rommel in that he lost the Atlantic shaft, a 2400-kilometer line of strengthening bunkers, ground mines and beach and water obstacles. In January 1944, General Dwight Eisenhuer (1890-1969) was appointed Commander Overlord Operation. Within a few weeks before the day, the Allies conducted a large disinforming operation, designed to force the Germans to think that the main goal of the invasion was the Strait of Pa de Kale (the most narrow place between the United Kingdom and France), and not Normandy. In addition, they forced the Germans to believe that Norway and several other places are also potential intrusion objects. To implement this false operation, the layouts of guns were used, the phantom army under the command of George Pattone and allegedly based in England, opposite Pa-de-Calais, double agents and radiograms with false information. Loaning landing in Normandy because of the weatherOn June 5, 1944, he was appointed in the afternoon of invasion, but Nature made its adjustments to Eisencura plans, the possession was postponed for a day. Early in the morning of June 5, a regular meteorologist of the Allied Forces reported on improving meteorological conditions, these news became defining and Eisenhower gave good to Overlord surgery. He told the troops: "You go to the Great Crusade, which we all prepared for many months. The views of the whole world are directed at you. " Later on the same day, more than 5 thousand ships and landing and landing facilities, carrying troops and guns, came out of England on the strait to France, and more than 11 thousand aircraft flew from the air from the air. Tentization per dayAt dawn on June 6, dozens of thousands of paratroopers and parachutes were abandoned in enemy rear, break bridges and trips. The landing land at 6:30 am. British and Canadians three groups easily overcame areas of the beaches "Gold", "Juno", "Sort", Americans - the site "Utah". The US Army and Allies collided with the fierce resistance of German soldiers at the Omaha plot, where more than 2 thousand people lost. Despite this end of the day, 156 thousand allied troops successfully stormed the beaches of Normandy. According to some estimates, more than 4 thousand soldiers of the allies killed on the day, and about a thousand were injured or disappeared. The Nazis desperately resisted, but on June 11, the beaches were completely over the control of the US Army, and the soldiers of the American army 326 thousand people, 50 thousand cars and about 100 thousand tons of equipment were huge in Normandy. Confection reigned in the German ranks - General Rommel was on vacation. Hitler assumed that this is a cunning maneuver, which Eisenhaur wants to distract Germany from the attack north of the Seine and refused to direct the nearby divisions for counterpart actions. Reinforcements were too far, which would cause a delay. He also hesitated, tighten the tank divisions to help. Effective aviation support for the offensive of the allies, did not give a head to the head, and the undermining of key bridges made the Germans make a hook a few hundred kilometers. Huge help was provided by the ship artillery, which was constantly ironing the shore. In the following days and weeks, the union army made his battles through the Bay of Normandy, the fascists had already understood the entire deployment of their position, so they resisted incredibly desperately. By the end of June, the Allies captured the vital port of Cherbourg, which allowed them to overdue the troops, 850 thousand people and 150 thousand cars were additionally arrived in Normandy. The army was ready to continue his victorious procession. Victory in NormandyBy the end of August 1944, the Allies approached the River Seine, Paris was released, and the Germans were knocked out from the north-west of France - the battle at Normandy was actually completed. The road to Berlin opened before the troops, where they had to meet with the troops of the USSR. The invasion of Normandia has become an important event in the war against the Nazis. The US attack made it possible to freely sigh with Soviet troops on the Eastern Front, Hitler was psychologically broken. The next spring, May 8, 1945, the Allies officially accepted the unconditional surrender of Nazi Germany. Weekly before, April 30, Hitler committed suicide. Author Vladimir Chelovov. Let's think that it would be if the Western Allies once again were proclaimed and did not land the landing in 1944? It is clear that Germany would still be divided, only the Red Army would finish the war not under Berlin and on Oder, but in Paris and on the shores of Loire. It is clear that General de Gaulle, who came to power in France, and anyone from the leaders of the Comintern. Similar figures would be found for Belgium, Holland, Denmark and all other large and small countries in Western Europe (as they were found for countries in Eastern Europe). Naturally, Germany would not be divided into four occupation zones, therefore, a single German state would have formed not in the 90s, and in the 40s, and it would be called not Germany, but the GDR. It would not be in this hypothetical world and a place for NATO (who would have entered in except the United States and England?), But in the Warsaw Agreement would unite the whole Europe. Ultimately, the Cold War, if she had taken place at all, would be a completely different character, and would have a completely different outcome. However, I'm not going to prove at all that everything would be exactly the case, and not otherwise. But in the fact that the results of the Second World War would be different, no doubt. Well, the battle, which largely identified the course of post-war development, should be considered the main battle of war. That's just a battle you can call it with a big stretch. Atlantic Val. Think by yourself what sense to have concrete fortifications on the very shore? Of course, the guns installed there can fire landing vessels, and machine-gun fire can be hit by the enemy soldier when they wander the belt in the water. But the bunkers standing right on the shore are perfectly visible to the enemy, so he without much difficulty can suppress their ship artillery. Therefore, directly in water cuts are created only by passive defensive structures (mine fields, concrete fores, anti-tank hedgehogs). Behind them, it is desirable for the ridges of a dune or hills, the trenches are broken, and on the reverse slopes of the hills, blockbinds and other shelters are built, where the infantry can wait for art narrow or bombing. Well, even further, sometimes a few kilometers from the coast, closed artillery positions are created (here it is here that you can see the powerful concrete chamsis, which we like to show in the movies so much). Approximately the plan and defense was built in Normandy, but I repeat, its main part was created only on paper. For example, mines were exhibited about three million, but at the most modest calculations needed at least sixty million. Artillery positions were mainly ready, but the tools were installed far from everywhere. I will tell such a story: long before the start of the invasion, the French resistance movement reported that on the Merville battery, the Germans installed four sea 155-mm guns. The shooting range of these guns could reach 22 km, so there was a danger of shelling warships, so it was decided to destroy the battery at any cost. This task was assigned to the 9th battalion of the 6th parachute division, which was preparing for her almost three months. A very accurate battery layout was built, and battalion fighters day after day attacked it from all sides. Finally, the day D, with a big noise and gamar, the battalion captured the battery and found there ... four French 75-mm guns on iron wheels (the seasons of the first world). Positions were really made under 155 mm guns, but the Germans themselves did not have, so they put what was at hand. It must be said that the Arsenal of the Atlantic Shaft in general consisted mainly of trophy guns. For four years, the Germans methodically gone there all that they got from the broken armies. There were Czech, Polish, French and even Soviet guns, and to many of them had a very limited supply of shells. Approximately the same was the case with small armaments, either a trophy, or removed from weapons on the Eastern Front fell into Normandia. In total, in the 37th army (namely, it was the main severity of battle) 252 types of ammunition were used, and 47 of them were removed from production. Personal composition Did not go around the Führer his attention and ordinary composition. Take for example 70th infantry division, more known as the "White Bread Division". She fully consisted of soldiers suffering from various types of stomach diseases, because of which they had to be constantly on a diet (naturally with the beginning of the invasion of the diet it became difficult to obey, so that this division disappeared itself). In other parts, there were whole battalions from soldiers suffering from flat-painting, diseases of the kidneys, diabetes, etc. In a relatively calm atmosphere, they could carry a rear service, but their combat value was close to zero. However, not all soldiers on the Atlantic shaft were sick or cripples, there was a lot and quite healthy there, that was it only for 40 years (and in artillery and mostly served in the fifty-year-old). Well, the last, the most amazing facts of the native Germans in infantry divisions were only about 50%, the remaining half was all sorts from all ends of Europe and Asia. It was ashamed to admit to this, but there were a lot of compatriots there, for example, the 162nd Infantry Division consisted of the so-called "Eastern Legions" (Turkmen, Uzbek, Azerbaijani, etc.). Were on the Atlantic Valley and Vlasovsky, however, the Germans themselves were not sure that there would be some kind of prog. For example, the Commander of the Cherbourg Garrison General Schliben said: "It is very doubtful that we will be able to incline these Russians to fight for Germany in France against Americans and the British." He was right, most of the eastern troops surrendered to allies without a fight. Bloody Beach "Omaha" By the way, there was an interesting case, perfectly characterizing the combat spirit of the allies. A few hours before the start of the invasion, aerial deposits were planted in the depths of the German defense. Due to the error of the pilots, about three dozen parachutists were reset on the very shore near the bunker W-5. Some of them were destroyed, the Germans were captured by others. And at 4.00, these prisoners began to emerge the bunker commander immediately send them to the rear. When the Germans asked that it was so impatient, the brave warriors immediately reported that an arteephone preparation from the ships would begin, followed by a landing. It is a pity that the story did not keep the names of these "freedom fighters and democracy", issued an hour to start the invasion for the sake of their skins. Let's go back, however, on the scenery "Omaha". In this area, only one available area is 6.5 km available for landing (east and west of it for many kilometers to reach steep cliffs). Naturally, the Germans were able to prepare him well to defense, there were two powerful bins with guns and machine guns on the flanks of the site. However, the cannons from them could only fire the beach and a small water strip along it (from the side of the sea, the bins were covered with rocks and a six-meter layer of concrete). For a relatively narrow beach strip, the hills began, up to 45 meters high, whose ridge were separated by trenches. All this defense system was well known to the allies, but they hoped to suppress it before the landing began. The fire on the springboard was to lead two linkers, three cruisers and six destroyers. In addition, field artillery should shoot with landing vessels, well, and eight landing barges were redesigned to the installation for starting jet shells. In just thirty minutes, more than 15 thousand shells of different calibers were supposed (up to 355-mm). And they were released ... in white light as in a penny. Subsequently, the Allies came up with a lot of exclusion of the small efficiency of shooting, here and strong excitement at the sea, and the predestal fog, and something else, but in one way or another, nor bunkers, nor even trenches from the art crestrail. Even worse than allied aviation. Armada Bombarders "Libertor" dropped several hundred tons of bombs, but none of them fell not only in strengthening the enemy, but even on the beach (and some bombs exploded five kilometers from the coast). Thus, the infantry had to overcome the completely intact band of the opponent's defense. However, troubles for land parts began before they were on the shore. For example, from 32 floating tanks (DD SERMAN) 27 sank almost immediately after the descent on the water (two tanks got to the beach, three more were unloaded straight to the shore). Commanders of some landing bargains, not wanting to enter the sector heated by German guns (Americans at all the instinct of self-preservation is developed much better than the sense of debt, and all other feelings), have led the ranks and proceeded to unloading at depths of about two meters, where most paratroopers have been successfully tone . Finally, the first wave of the landing was planted. It included the 146th sapper battalion, whose fighters were needed, first of all, destroy the concrete fores, so that it was possible to start landing tanks. But it was not there, it was, for each superb laying two or three brave American infantrymen, who, to put it mildly, objected to the destruction of such reliable shelter. I had to lay the saules to lay explosives from the side facing the enemy (naturally, many of them were killed 111 from the 272 stems). For helping saperes in the first wave, 16 armored bulldozers were granted. Only three reached the shore, and the use of sappers were able to only two of them - paratroopers were hidden and, threatening the driver with a weapon, forced him to stay in place. It seems that examples of "mass heroism" is quite enough. Well, then we start with solid riddles. In any source dedicated to the events at the Omaha section, there must be a mention of two "fire-haired bunkers on the flanks", but not in any of them they say who, when and how to suppress the fire of these bunkers. It seems that the Germans shot-shot, and then stopped (perhaps, so it was, remember that I wrote above about the ammunition). It is even more interesting about the machine guns shifted on the front. When American sappers smoked their comrades because of concrete foreman, they had to seek salvation in the dead zone at the foot of the hills (in some way it can be considered an onset). One of the branches there were discovered a narrow path leading to the top. Carefully moving on this path, the infantrymen got to the ridge of the hill, and there were completely empty trenches there! Where did the Germans defeated them? And there was no place there, on this plot, the defenses occupied one of the mouth of the 1st battalion of the 726th Grenadier regiment, which consisted mainly of Czechs forcibly designed to the Wehrmacht. Naturally, they dreamed of surrender to the Americans as soon as possible, but agree, throw a white flag before the enemy attacks you somehow unoliginal even for the descendants of the brave soldier Schweik. The Czechs lay in the trenches, from time to time releaseing a turn-other towards Americans. But after a while they realized that even such a formal resistance restrains the offensive of the enemy, so they gathered manati and moved to the rear. There, in the end, they were captured to general pleasure. In short, shifting the pile of devoted to NDO materials, I managed to find one only story about a combat clash at the Omaha bridgehead, I cite him literally. "Rota" E ", landed before Collarm after a two-hour battle captured the German bunker on top of the hill and captured 21 people." Everything! Home Battle of World War II And escape from the European continent (), and landing in Normandy ("Overlod") are not very similar to their mythological interpretation ... The original is taken by W. jeteraconte In the landing of allies in Normandy ... myths and reality. I i think that every educated person knows that on June 6, 1944, there was an allied landing in Normandy, and finally, a full opening of the second front. T. how many estimates of this event has different interpretations. Why did the allies reach until 1944? What goals pursued? Why was the operation was carried out so non-readable and with such sensitive losses, with the overwhelming superiority of the allies? By 1944, all politicians were clear that the war of Germany and its allies were played, and in 1943, during the Tehran Conference, Stalin, Roosevelt and Churchill, roughly divided the world among themselves. A little more and Europe, and most importantly, France could become communist, if they were liberated by Soviet troops, so the allies were forced to rush to catch to the section of the cake and fulfill their promises to contribute to the general victory. (I recommend to read the "correspondence Chairman of the USSR Council of Ministers with US Presidents and the Prime Ministers of the United Kingdom during the Great Patriotic War of 1941-1945" released in 1957, in response to the memories of Winston Churchil.) Now let's try to figure out what and how it really happened. First of all, I decided to go and see my own eyes on the terrain, and appreciate what difficulties sitting under the fires, it was necessary to overcome. The landing area takes about 80km, but this does not mean that all the length of these 80 km, paratroopers were planted on each meter, in fact it was concentrated in several places: "Sord", "Juno" "Gold", "Omaha Beach" And "Pointed D OK." At all parts of the Allies suffered relatively small losses, except ... Mini Museum between disembarking zones:
View of Pont D Ok from above, funnels, remnants of fortifications, incidents.
Omaha Beach View of the sea and disembarkation area:
World War II. 1939-1945. History of the Great War of Chefov Nikolay Alexandrovich Allied landing in FranceAllied landing in France On June 6, 1944, the disembarkation of the Allied Troops on the North-West Coast of France, in Normandy. The upcoming invasion was impossible to hide. Therefore, the main question was where the landing began. The line of the French coast, which was over 2 thousand km, gave ample opportunities to select the landing area. It forced the Germans to spray their limited forces on a wide front. Time and place of disembarkation remained in deep mystery. For example, in coastal areas where they were ready for the invasion of troops, access for civilians was closed. Active work was carried out on disinformation regarding the invasion area. German intelligence failed to get the necessary information about the time and place of landing. As a result, the German leadership did not have accurate information. It was expected to land the allies in the Para de Calais Strait, where the distance between England and the mainland was minimal. The main forces were concentrated here, and also the most fortified part of the so-called "Atlantic Shaft" - a system of defensive structures in the French coast. Other areas were protected significantly weaker. The coast of Northern France, Belgium and Holland defended the German group of Army "B" under the command of Field Marshal Rommel as part of the 7th and 15th armies and the 88th individual corps. The general command of the German troops in the West was carried out by Field Marshal K. von Rundstedt. The expeditionary forces of the Allies under the command of General G. Montgomery united in the 21st group of armies (1st American, 2nd English, 1st Canadian army). The ratio of forces and means of the sides on the eve of the allied landing in Normandy From the table it is clear that the allies had an overwhelming superiority. The table took into account the German troops, which could be brought to reflect the landing, including from other areas of France. But in the air in the air of the Allied Aviation and the active actions of the French partisans, it was extremely difficult. However, the Allied troops were planted in France at the same time. Allied landing in Normandy (Overlord Operation) was a complete surprise for the German command. On the night of June 6, under the cover of massive blows of aviation, two large air landings were landed (up to 18 thousand people), which tried to block German communications, under the cover of the massive blows of aviation north-east of Cannes. With the onset of dawn, aviation and ships allies poured the North Coast of Normandy Grad Aviabomba and shells. They suppressed German batteries, destroyed defensive structures, swept the wire barriers, destroyed the mine fields and damaged the links. Under the cover of this powerful fire, landing ships approached the shore. On the morning of June 6, sea pags were planted at a 100-kilometer plot between the River ORN and the eastern part of the Cotangen Peninsula. They captured 3 large bridgeheads depth from 2 to 9 km. For disembarking, over 6 thousand warships, transport and landing ships were used. Thanks to the successful actions of surface ships and aviation, the Germans failed to use their superiority in submarines to prevent the delivery of troops and cargo. On June 6, the allies landed 156 thousand soldiers on the coast, and more than 20 thousand units of equipment were delivered to seized bridgeheads. It was the largest landing operation of World War II. German forces located in this area were far from sufficient to provide serious resistance to numerically superior allies compounds. In addition, the German command did not immediately figure out the situation, continuing to consider the landing in Normandy distracting maneuver. Hitler, convinced that soon in the area of \u200b\u200bPa-de-Cala, the main landline will land, forbid it at first to put forward large reserves in Norman. This forenoading opinion, the German top command firmly adhered to within a few days. When, finally it became clear that the case is about a serious large-scale operation, the precious time was missed. The allies entrenched on the bridgeheads, and knock them out from there with the existing ratio of forces and funds in Germans there were very little chance. Nevertheless, thanks to the gradual tightening of reinforcements, the number of German troops was brought to three infantry and one tank division in the coming days. This allowed them to provide stubborn resistance. But it could not hold back the excellent allies forces, with the support of ship artillery and aviation, it was possible to establish a link between the bridgeheads. By June 10, one bridgehead was created from them, which had over 70 km on the front and 10-17 km in depth. By June 12, the number of troops on it reached 327 thousand people., 5,400 aircraft, 104 thousand tons of military equipment and equipment. Reset such a lot of people and techniques in the sea Germans who did not have serious support for tanks, aviation and artillery, it was almost impossible. The main efforts of German troops now walked to hold the promotion of the allies as long as possible and do not give them to the operational space. The bridgehead in the meantime expanded. June 18, the 7th US Corps reached the western coast of Cotanen Peninsula. As a result of this operation, the port of Cherbourg is isolated on the northern tip of the peninsula. By June 21, the Americans approached the Cherburo and after powerful aviation training began the storming of the fortress. On June 27, her garrison folded the weapon. Shortly after the allied landing in Normandy, the Germans began the shelling of England with their new weapons - FAU-1 loafers. Hitler was held for three years to have a huge cost, developing a long-range missile program, whose target was to become London and southern English ports. In mid-June 1944, the first shelling of London took place. At the end of the summer, an even more powerful FAU-2 missile appeared. For seven months, the Germans were released on London 1,100 FAu-2 missiles, and in Liege and Antwerp - 1675 missiles. However, the new weapon did not give the effect to which the leaders of the Reich were expected, and could not seriously affect the course of the war. By the end of June, the bridgehead on the coast of Normandy reached 40 km deep and 100 km in width. There were 875 thousand soldiers and 23 airfield on it, which resulted in a significant part of the Union Aviation. The bridgehead now had a large port of Cherbourg, who after recovery (in the first half of July) began to play a significant role in the supply of union troops in France. 18 German divisions acted against a bridgehead at the front of 100 km. It was a very high defense density. However, these German divisions experienced a shortage of personnel and combat equipment, and also endured a serious damage from powerful strikes of artillery and aviation. It was still not decided to increase their forces in Normandy Hitler yet due to the fear of landing the second landing in Pa de Calais. There were no largest reserves in France. The main forces of the Wehrmacht fought on the Eastern Front, where at the time the powerful offensive of Soviet troops in Belarus began. By July 1, the German command was forced to state that it was not possible to cope with the enemy grouping in Normandy and would not succeed. However, the attempts of allies expand the bridgehead in July in the month of the past resistance to the German parts. From June 25 to July 25, the front in Normandy shifted only 10-15 km. The most cruel fighting in July turned over the nodes of the roads - the towns of Saint-Lo and Cannes. The complete superiority of the allies in the air was combined with a clear interaction of the army and aviation. This is how the Arnold General describes the promotion of American troops on Saint-Lo: "Fighters and fighter-bombers, supporting the most direct connection and acting under the general command, flew ahead, hitting military purposes. Supporting direct radio communications with tanks, fighters in constant combat readiness were licked over our tank columns. Officers from the Earth caused fighters for bombing or shelling on the way of artillery or tanks. The pilots warned tank commanders about anti-tank traps. " Without air support, German troops nevertheless were not going to retreat and fought steadfastly. They created deeply echelonized defense provided by a large number of anti-tank agents. Despite the air support 2000-2200 bombers, take this resistance node only after numerous attacks. Saint-Lo fell on July 18. On the same day, the strongest tank blow was carried out under Canned. It was attended by three armored divisions of the Allies at once. They switched to the offensive after intense bomb strikes, which caused 2 thousand bombers. These strikes were so powerful that most of the prisoners stunned by breaks, almost a day could not even answer questions. It seemed that the allies were doomed to the success of a breakthrough and access to operational space. However, the defensive of the Germans turned out to be much deeperly echelonized than the union command assumed. Cannes lasted another three days and fell on July 21 after fierce fighting. By July 25, the Allies went on the line of Saint-Lo, Comon, Cannes. At this, the Overlord operation ended. Allies lost about 122 thousand people in it., Germans are about 117 thousand people. Slow promotion of allied armies in July did not justify great hopes that appeared after the successful landing. The bridgehead, captured during the operation in Normandy (up to 110 km on the front and a depth of 30-50 km), was 2 times less than that it was envisaged to take the operation plan. However, in the conditions of absolute domination in the air, the Allies could be easily focused on sufficient forces and means for holding a large offensive operation. The difficult position of the Germans on the front was aggravated by the disorganization of their senior command. Allied landing in Normandy and the defeat of German troops in Belarus caused a political crisis in Germany. He expressed himself in an attempt to the state coup, which organized the Military dissatisfied with Hitler. The conspirators were assumed to physically eliminate the Fuhrera, seize power, and then conclude peace with all the countries of the anti-Hitler coalition. The murder of the chapter of the Third Reich was entrusted to Colonel Staugenberg. On July 20, he left the room where Hitler conducted a meeting, a portfolio with a delayed action bomb. But the explosion caused only small destruction, and the Führer stayed alive. Conspiracy failed. His organizers were captured and shot. The case of Staugnberg negatively affected the moral state of the officer's corps of Germany, giving rise to the fear of repression in its ranks. Meanwhile, the allies were preparing to go into a decisive offensive. For this, they had 32 divisions, 2.5 thousand tanks and 11 thousand aircraft. They opposed 24 German divisions that had about 900 tanks that had a weak air cover. The offensive began in the morning of July 25, with Moshnaya Aviation Preparation. 4700 tons of bombs were reset to the area of \u200b\u200bthe alleged breakthrough (8 and width of 1.5 km). Using this knockout bomb strike, the Allied Divisians rushed forward. By the end of the third day, German defense was broken by the entire tactical depth (15-20 km). Pursuing the retreating German parts, the Allied troops came to the operational space. In an effort to stop this breakthrough, the Germans were thrown into battle reserves. But in vain. The attempt of the German counterdad on August 8 in the Morten area with the aim of abrupting the coming troops failed. A significant role in the failure of the Germans played a lack of spruce and massive blows of allies on tank columns. Without reaching the goals, Consturdar under Martin turned into a serious problem for German troops. He detained their departure until the Allied troops accounted to the flanks of the contrasting German parts. After the failure of Kontrudar under Mortin, a significant part of the German troops stuck to the west of the Seine was cut off from the mainstream and landed in a bag in the area of \u200b\u200bFaleza. Meanwhile, the Commander from the beginning of July, German troops in France Feldmarshal Belyle took his surviving army for the Seine. He sought to quickly escape from the trap, in which they were due to the ban of Hitler to move away from the positions occupied. Due to the insufficient coordination of the actions of the allies, the main forces surrounded managed to break into the east through the corridor between Argenthan and Falez. Although the bulk of August 19 broke out of the phalevsky bag, about 50 thousand Germans still captured, and 10 thousand died in battles. As a result of the Allied breakthrough from Normandy, the German front in Northern France was splitting. His eastern part continued to depart to the borders of Germany, and the Western group (up to 200 thousand people) turned out to be cut and pressed against the West Coast of France. Most of the sliced \u200b\u200btroops sat down in the garrisons of coastal cities-fortresses. Some of them (in Lorient, Saint-Node, etc.) continued to resist until the end of the war. On August 16, Hitler removed the clue from the command and appointed the Feldmarshal model in his place. But the new commander could not significantly correct the situation. On August 25, allied troops reached the Sena and entered into the capital of France Paris, freed on the day before during the national uprising. On the eastern bank of the river was captured by a bridgehead in the Ovre district. During the offensive in Paris, the Allies on August 15, 1944 landed a large landing in southern France, between Cannes and Toulon. There was a 7th American army under the command of General A. Patcha. It included tested parts that had experience in battle in North Africa and Italy. The landing of the landing provided about 700 warships. By August 19, allied troops created a bridgehead to 90 km on the front and up to 60 km deep. It was concentrated to 160 thousand people., 2500 thousand guns and 600 tanks. The Americans have learned lessons from their previous landing operations and refused the principle of occurrence with a plannedly prepared bridgehead. Now all the landed troops, without losing time, moved as follows as follows. In the south of France, the 19th German Army (10 divisions) was poorly staffed and had low combat capability. Her troops who carried large losses from strikes of artillery and aviation, could not have any significant resistance anywhere. They started hasty departure to the north, seeking to avoid the environment and defeat. Overcoming minor resistance, the allies occupied Marseille and began to move along the Rhone Valley. For 8 days, they advanced ahead of 225 km. The German 19th Army retreated to Belforge. By September 10, the allies coming from the south were connected in the Dijon area with divisions of the 3rd American Army. As a result, a single front of the Allied Troops in the West was formed. The initial model of the model to defend the Northern Coast of the Seine turned out to be impracticable. I delayed a little at this turn, the German army, which preserved combat capability, retreated to the new line of defense at the borders of Germany. In early September, the command of the German troops in the West again accepted Field Marshal Rundstedt. Feldmarshal The model was only the commander of the Army Group "B". At the same time, the leadership of all land operations of allies in the West was headed by General D. Eisenhuer. On the left flank allies, the 21st group of armies were advancing under the command of Field Marshal Montgomery (1st Canadian and 2nd English Army). In the center of the 12th Army Group under the command of General D. Bradley (1st, 3rd and 9th American Army). On the right flank - the 6th Army Group under the command of General D. Divers (7th American and 1st French Army). Pursuing the retreating German parts, the allies joined the territory of Belgium. On September 3, they occupied Brussels, and the next day, almost without battle entered Antwerp, where they got completely preserved port facilities. France's liberation in general was completed. The total number of union troops on its territory exceeded 2 million people by that time. Hitler's dream about the impregnable "Europe fortress" collapsed in his eyes. The war approached the turns, from where she came four years ago. Having received the place of basing in France, the Allies continued to be an air offensive to Germany. Thus, the English bombarding aircraft for June - August dropped about 32 thousand tons of bombs on the territory of Germany. During the same time, the 8th American air army dropped about 67 thousand tons of bombs to objects in Germany. These powerful bombings led to a reduction in industrial production in Germany and its satellites. Thus, the production of fuel in Germany and the allied states was 32 percent in September of the beginning of the early summer of 1944. During the battle for France, German troops suffered a crushing defeat. They lost almost half a million people. The losses of the Allies amounted to about 40 thousand people. Killed, 164 thousand wounded and 20 thousand missing. By mid-September, the German command was located on the Western front with only 100 combat-ready tanks against 2000, acting as part of the first echelons of the Allied Forces, and 570 aircraft (there were 14 thousand of them allies). Thus, the Allied Army exceeded the Germans 20 times in tanks and almost 25 times on aircraft. These stunning successes made such a strong impression on Montgomery that he turned to Eisenhauer with a request to provide him with a sufficient number of equipment for breaking up to Berlin himself. Such optimism had a good basis. According to the memoirs of the German general of Bluemenitrite, at the end of August 1944 the German front in the West was actually open. When, in early September, the allies approached the German borders, the Germans did not have for the Rhine major troops, and nothing could delay the promotion of allies deep into Germany. However, when the victory seemed completely close, the pace of allone troops fell sharply. There was a significant reason for their slowdown, there were interruptions with separation of fuel. The communications of the allies stretched out, and the system parts were far away from the bases of the rebar. The troops experienced an acute fuel shortage. No less serious brake was the resistance of German troops. In the critical situation of the first half of September, the subtle line remained in the ranking parts of the Wehrmacht at the cost of incredible efforts covered the path to the Rhine and continued to hold the position before the approach of the necessary reserves. As a result of the throw for the Rhine did not come out. The last hundred kilometers on the way to this river Allies had to overcome almost six months with great efforts and losses. From the book World History. Volume 2. Middle Ages by Yeger Oscar From the book Russia in the war 1941-1945 The author vert AlexanderChapter V. Political events of the Spring 1944 of the USSR and allies landing in Normandy by mid-May 1944. The Soviet-German front has occurred a period of relative lull. Now the front (with the exception of the huge Belarusian protrusion in the center, where the Germans were still inclined From the book History of the Russian Army. Tom Third Author Zaisonchkovsky Andrey Mochordovich From the book History of World War II Author Tippelskirch Kurt Background From the book is neither fear or hope. Chronicle of World War II by the eyes of the German general. 1940-1945 Author Zenger Frido BackgroundThe landing of the allies landing on July 10 did not become a surprise. Here are the excerpts from the magazine of the hostilities of the German Communications Mission at the 6th Italian Army: "July 9, 18.20. In radio communication from the 2nd Aviation Corps, the six conversions of the total number of 150-200 vessels in the waters From the book Secret Questions of RSH by the author Sorrow OttoThe landing the next day - and it was Sunday on September 12, 1943 - we go on five in the morning at the airfield, where it turns out that the gliders will be at about ten. I took advantage of this deferment to check out the equipment of my people once again. Each of them From the book Millennaya Battle for Tsargrad Author Wigsaw Alexander BorisovichChapter 4 Allied landing in Crimea The defeat of the Turks in Sinop accelerated the entry into the war of England and France. December 22, 1853 (January 3, 1854) United Anglo-French fleet entered the Black Sea. Three days later, English steamer "Retribushen" approached Sevastopol and announced From the book of War on the Sea (1939-1945) author Nimits ChesterDragun operation - landing in southern France after a while after the class of Rome's allies (and it, as we remember, almost coincided with the invasion of Normandia), three American and two French divisions were withdrawn from the Italian front to participate in the operation "Dragun" From the book Chronicle of Air War: Strategy and Tactics. 1939-1945 Author Alyabyev Alexander NikolaevichChapter 9 Kursk Arc. Disembarking allies in Sicily. The beginning of the Italian campaign July is December, July 1, 1943. Secret report of the SS security service on internal political situation No. 410 (excerpt): "I. Common. The proliferation of rumors about new weapons and From the book History of World War II. Blitzkrieg Author Tippelskirch Kurt Background7. The landing in southern France by the time when the defeat of the group of the army "B" found its obvious symbolic expression in the loss of the French capital, the situation in southern France also changed radically. On August 15, Eisenhuer appointed a long time already scheduled and From Blitzkrieg's book in Western Europe: Norway, Denmark Author Patney Sergey Vladimirovich From the book, the influence of sea strength on history 1660-1783 by Mahan Alfred. From the book Chronology of Russian history. Russia and world Author Anisimov Evgeny Viktorovich1944, June 6, the beginning of the Overlord operation, the allied landing in Normandy Allies (Americans, the British, Canadians, as well as the French and Poles) quite a long time prepared for this unparalleled landing operation, in which more than 3 million people participated. Experience was taken into account Author2.2. The decisive attack of the fascist block in the summer of 1942, the allied landing in North Africa instead of the opening of the second front Stalingrad - the beginning of the indigenous fracture The fascist block is torn to the victory at the Main Theater of Warsckers "Blitzkrieg" near Moscow set Germany and From the book of the defeat of fascism. USSR and Anglo-American allies in World War II Author Olschtynsky Lennor Ivanovich2.3. 1943 The promised second front is postponed by the Kursk battle - a radical fracture in World War II, landing allies in Sicily, anti-fascist struggle in Italy offensive operations of the Soviet troops and allies in winter - in the spring of 1943. Constressation under From the book of Crimean War, 1854-1856 Author Dukhlnikov Vladimir MikhailovichLanding allies on the Crimean Peninsula. The first battles of the ships of the United Socadron in the Black Sea coast of Russia appeared on 8 (20) of April 1854 and stopped three kilometers from Odessa. On April 22, 9 enemy ships approached the shore and began bombing Extruding of the Allied Troops in Normandy
|
Popular:
New
- Hydrogen Communication All Examples
- Barbaric Encyclopedia: Commod, Emperor Lucius Ely Aureli Commoda Mark Azeri Son
- History of creation and development
- History of the emergence of information resources of society
- How the intelligence officer Nikolay Kuznetsov killed (5 photos) Neither Kuznetsov
- Novgorod land (Republic) Culture of Novgorod land in the 12th century
- Poisoning arsenic and its salts - fatal dose for man, symptoms, treatment
- LOST - Railway station overcome whether "Human Factor"
- Essence and principles of collectivization collectivization in the USSR causes essence results
- Socialization hazards. Social hazards. Classification of social hazards. Brief description of the main types of social hazards