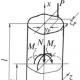
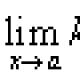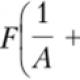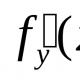Sections of the site
Editor's Choice:
- Weightless life: as astronauts sleep, eat and certify the need for the station
- "Heroic landing" allies in Normandy
- Four kingdoms of wildlife
- The main riddles of the history of Russia
- "Heroic landing" allies in Normandy (12 photos)
- Major instincts. Hunting and gathering. Three main instincts
- The brightest planet. For all and about everything
- Which planet is the brightest in the sky
- Armion Spaws and Travel
- Russian spirit!!! Great Rus !!! Nice feats of Russian warriors
Advertising
| Abstract "The history of shipbuilding development in Russia". Tutorial The abstract of lectures on the discipline "The History of Maritime |
|
In the XV century, a new type of ocean sailing ship appears - Karavella. This vessel has become known to all of Europe after Christopher Columbus immortalized his name to the opening of America. Flotilla Columbus and consisted of three caravel. Until that time, so-called small impaired vessels. Therefore, some historians were deeply mistaken, arguing that Columbus reached the shores of America "on shells". True, the length of its large caravella "Santa Maria" was about 25 meters, and a small "nigni" - only 18. But it was very light on the go and very nautical deck courts with superstructures in the nose and especially on the stern. In the superstructures and placed the crew. These caravellas were much stronger and rushing than the largest oils and storms, although the load took much less. When Columbus in the summer of 1492 left the port of Palace in historical swimming, on board his Karavella Pinta was 80 people and a huge supply of provisions, equipment and fresh water. And the whole Karavel could take 120 tons of cargo. Columbus, describing a storm, which covered it on the way back in the Azores, said that he got rid of death only thanks to a strong design and good nautical qualities of his caravel. By the way, in 1892, when the 400th anniversary of the opening of America was celebrated, the organizers of the celebrations came up with such a thing: they decided to build the most real caravel, in everything similar to Columbovskaya, and on it exactly to repeat the historical flight Columbus. So done. And again solemnly "opened America" \u200b\u200bafter the ocean transition, perfect well safely. The difference was only that "just in case" there was a huge steamer all the time! In the XVIII century, England, then "Lady of the Seas", in the first place for the construction of sailing vessels. This was largely helped by the fact that the British ships were built from the primitive Russian materials exported from Arkhangelsk. So, the sails of the British sewed from the Russian canvas. The masts were made from trees that grew up in Russian pine forests. Tackle was manufactured from Russian hemp. When the anchors and chains were killed, the transshipment of the Ural Iron was heard. But how was the development of the Russian sailing fleet? It leads its beginning from the XI-XII centuries. Already the Fleet of Novgorod the Great consisted of a variety of sailing vessels. In 1948, during the excavations, the old Ladoga discovered the remains of an ancient ship. These remnants tell us about the high mastery of shipbuilders of Novgorod. On the ribs-splint sets, preserved from this nautical set area, the traces of wooden nails are clearly visible. Back in the XII century, Novgorod committed distant swimming in the Baltic Sea, reached the ports of Sweden and Denmark. In the Russians, mentions were preserved about the time when the merchants - "Guests of Novgorod" - and their "squalls brave" "were guarded on the blue-sea Varyazhsky", "walked along the Volga and ran across the sea volatile" ( Caspian Sea). Novgorod reached even to the White Sea and here, on the coast, they founded several settlements. Tatar-Mongol invasion, and then the Swedish-German invasion in the north-west was deprived of Russia to enter the seas. For several centuries, the development of the Russian fleet was interrupted. Washing at this time developed only in the north of our country. Descendants of the Novgorod residents - Pomor - felt at the "Sea of \u200b\u200bStuden", like at home. Moreover, they walked for the fishery of the beast and fish to the newest land and even penetrated the Kara Sea. They used to visit the island of Spitsbergen, before foreign navigators. Pomor built wonderful sea vessels. Fearless earthquakes went out on the lungs of anticipate ears. And a little later appeared and already familiar to you one-way chambers. They were flat-bottom, singleal-chain ships of about 20 meters long, with durable, adapted for swimming among ice, housing. Most often, Kochi walked under the sail. Quadranular sail for a long time stitched from the skins; Tools were belt. To build such a vessel, the skillful Morelodam did not require a single iron part. They say that even the anchors did from Koryagi, tied to it a stone sniffer. Of course, over time and Koch has changed, iron mounts appeared. Pomor was built and three-person sailing vessels - naval turbines, which raised to 200 tons of cargo. Floating on such vessels, Russian nautical seats at the end of the XVI and early XVII century opened the world of the Northern and Eastern shores of Asia. And Semyon Semen Dejnev first in 1648 passed between Asia and North America. By this, he proved that there is a strait between both continents. But scientists of Western Europe were considered that Asia and America are some of the mainland. In the XVII century, the construction of individual sailing ships of large sizes on the overseas fellow begins. The first such ship is a three-volume, still flat "Frederick" ("Friedrich") - was built back in 1635 in the lower The second attempt to create a fleet from large sea ships was made with Alexei Mikhailovic on the Volga - in the village of Dedinovo. A large three-volume eagle was built here. He also suffered a sad fate: Stepan's troops Razin took Astrakhan and burned the "eagle" there. Only under Peter I began to create a strong marine fleet. In the hall of the Central Naval Museum there is a small bot. This ship has played a very large role in the life of Peter I and in the history of the Russian Fleet. For no accident, this old-fashioned ship is respectfully called the "Grandfather of the Russian Fleet". Rushing on Jauze on this boot, the young Peter caught fire to the sea and the marine case. The shores of the river seemed close. He suffered a bot on Pereyaslavl - Plescheyevo Lake, built there a few more dozen shipyushki and conducted entire "maritime battles" with his "funny" flotilla. These games of the young king were harbing a great deal. This case was the creation in our country of the military and merchant fleet and the conquest of entering the sea. Russia occupied the honorable place in a number of great nautical powers. During the reign of Peter 1, a strong combat fleet was created, consisting of 48 powerful linear ships and frigates, 790 gallery and other sailing and rowing vessels. The American marine historian Mahen called it a "unique historical miracle." Much attention was paid to Peter I Development of the Fleet and Shipping. He visited Arkhangelsk three times, sailed in the White Sea; She visited the ship shipyard of the Bazhenin brothers on the Wavcuga River. Large shopping ships were built on this shipyard. In 1703, the first such vessel "Andrei Varozvannaya" went with Russian goods to England and Holland. And in the same year the first foreign ship came to St. Petersburg. And on the last year of life, Peter more nine hundred ships visited the port of the young capital. Russian Linear ship of Petrovsky time - Poltava. A quick growing Russian fleet took many sailors and shipbuilders. Peter I sent abroad a large group of young people to teach their sea case. He himself over four months worked as a carpenter on shipyard in Amsterdam and studied the theory of shipbuilding under the leadership of the best masters of Holland and England. In Moscow, it was created in 1701 "School of Mathematical and Navalskikh Science", and in St. Petersburg in 1716, the Marine Academy opened. With Peter I, for the first time about twenty tranquits and shipbuilding textbooks were published. Peter I took a lot about improving the courts under construction. The successors of Peter I paid a little attention to the development of the fleet, and the construction of the courts strongly declined. Only with Catherine II, shipbuilding at the time took the previous scope. You can call many names of talented Russian shipbuilders. True, most of them had to build mainly combat ships, but many of them were distinguished in the construction of commercial ships. So, ordering on the Wawchug shipyard of the court, the British and the Dutch specifically paid a lot of money for making it necessary to build himself Stepan Kochenev. Self-taught, friend of Lomonosov, Stepan Kochev became famous for "strong and with special art of the construction" of large naval vessels. Arkhangelsk Master M. D. Portnov for twenty-three years of work built sixty-three ships. A. M. Kurochkin worked at the beginning of the XIX century, too, in Arkhangelsk. He created such durable and beautiful vehicles such that the order came from the government to "engrave to edify the offspring the drawing of this corps on copper, to preserve it in the immutability." Contemporary Kurochina - Ivan Afanasyev was famous for his work on the Black Sea. For his life, he built 38 large and many small combat and merchant ships. The Russian flag began to appear in the most distant and still few hungry corners of the globe. Great merit of Russian sailors. In the XVIII century, they explored the shores of North-West America. In the XIX century, they were 42 around the world, during which important geographical discoveries were made. Many work was put on the discovery and study of the shores of the Pacific Ocean and the Arctic, such famous seafarers, like Bering, Chirikov, Golitan, Nevelsky, Cruise, Litch, Malygin and others. At the beginning of the XV century. One of the largest vessels of the cargo was a storm. It was characterized by a high tank, the presence of several longitudinal mounts, and two or more decks were located on the quarters. Compared with the modern ships, the carrying capacity of the Karaki was truly impressive: the biggest of them could accommodate up to 2,000 tons. At the same time, the vessel was well armed: on board it was usually from 30 to 40 guns. There were three masts on the ship: in the middle, the grotto Mast was installed with a large rema, on which a straight sail was fixed, on the stern - Bizan Mast, equipped with a Latin sail, on the nose - a fock mast with direct sail, and on the tank - a bushchite. Advantages of medieval galleysThis era did not exist with a clear differentiation between trading and military ships: for centuries, only a rowing gallery was considered exclusively a military ship. For example, the Venetian gallean had the following dimensions: width - 5 m, length - 40-50 m, the distance from the deck to keel - approximately 1.8 m. From each side of the gallers were 26-30 cans, which were installed at a certain angle to board. On the bank could accommodate 3 rower, each of which had their own paddle. As a rule, there were two masts on the gallery: the fock mast on the nose of the ship and the grotto mast, located at a resistant of the vessel's length, ranging from the nose. Latin sails were fixed on both masts. Ships - Direct Heirs GalelThe successors of galleys were a high-speed Fust, for each bot for which there were 18-22 jars for rowers, Galiota (14-20 cans), Brigantine (8-12 cans), light frigate Saeta - direct precursor of a three-volume shopping ship, distinguished by the presence of Latin sails to the bizan - And the grotty mast and direct sail on the Fock Mast, and the well-known frigate (6-20 cans). Galeasi stand out even greater length than galleys: they could reach 70 m. Their features include the presence of three masts and 32 cans for each of the sides that were under deck. The upper part of the deck was assigned under. Construction of ships in the XVI century.By the middle of the XVI century. A large sailboat having 3 or 4 masts is now called just a vessel. In this class, one of the most famous was the ship of Henry VIII called "Henry Grace E" Dew ". This vessel had a loading capacity of about 1,000 tons, and his cover was still made by Vnakroy. On the ship could be free to accommodate 900 crews, which served 195 Tools. His feature was four masts, equipped with walls, on a fodder mast there was only one wall.  In Northern Europe in the XVI century. Pinas originated - a new type of ship, a little resembling galleas. Its displacement ranged from 150 to 800 tons, the vessel was three-person, but only the grotto was equipped with Marseille. Galion can be attributed to the same class - the Portuguese warship. Later, Galione was equipped with English and Spanish fleet. The ship was distinguished by a rather sharp body, and his length of Kil was three times more than its width. For the first time on the vessel of such a model, the guns were installed not only above, but also under the main deck and fired through the ports. The long housing and low superstructures provided Galion to the greater speed and the ability to walk at a large angle to the wind than the "round" ships. 1. Historical shipbuilding development From time immemorial, people used water expanses - rivers, lakes, the sea - first as hunting grounds, and then as comfortable roads for moving and transporting goods. The first primitive vessels appeared for a long time to the wheel wagon. The man came out at sea at the dawn of his formation. Mythology Vintage Travel Descriptions and Saga allows you to collect information about the courts. Sometimes they are quite detailed in them to the construction and equipping the "first ships", indicating that they built their people by the will of the gods. This is the case with a noah ark. Oldest Chelny Namerheil from Pessa, Granking (Netherlands), -6315 + 275 BC Already about 2500 years BC. Courts were different: for the carriage of goods, for the transport of passengers. They were driven by poles, oars and sails. In those days, the vessels were mainly military, shopping or fishing. Later appeared vessels for recreation, on which they swam, just for the sake of entertainment. Such a vessel Roman Emperor Caligula (37 - 41 years .: AD) ordered to build for his fishery trips to Lake Nali. An unusually wide and flat design of the vessel is explained by its appointment: a ship for courtiers. The case itself was dialed out of wood, and hollow beams made of burned clay were used as a pitch of the upper deck. To ensure the impermeability and preservation of the vessel, the outer sheat board were covered with lead plates, the inner flooring consisted of marble tiles. In Russia, shipbuilding and navigation were known from the most remote times. Fashionable drawings dating from about 3000 years BC, depicting hunting with harpoon on the marine beast met on the coast of the White Sea. One of the oldest courts found in Russia dating about 5V. BC. In all Slavic languages \u200b\u200bthere is a word ship. His root is "bark" - underlies such words as "basket". The oldest Russian courts were made from flexible rods, as a basket and were trimmed with a bark (later - leather). It is known that already in the 8th century. Our compatriots swam in the Caspian Sea. In the 9th and first half of the 10th century. The Russians were the full owners of the Black Sea, and not in a gift at the time the eastern peoples called him "Russian Sea". At 12 in. For the first time, deck courts were built on Rus. Decks designed to accommodate warriors at the same time served as protecting rowers. Slavs were skilled shipbuilders and built vessels of various designs: Schitik - a flat-bottomed ship with a mounted steering wheel equipped with a mast with direct sail and oars; Carbas - equipped with two masts that carry straight rail or sprinkle sails; Pomeranian Lady - had three masts that were carrying on a straight savory; Rowish is a vessel, where the housing in the underwater part had an ovoid shape. Due to this, when compresseding ice, among which it was swimming, the vessel "squeezed" to the surface, without exposing the deformations and was immersed again in water during the diverge to the ice. The organized maritime shipbuilding in Russia began at the end of the 15th century, when the shipyard was founded in the Solovetsky monastery for the construction of commercial ships. Later already in 16-17 centuries. A step forward was made by Zaporizhzhya Cossacks who committed a raid on the Turks on their "seagulls". The construction technique was the same as in the manufacture of Kiev Nabe Ltodel (in order to increase the size of the vessel to the bottom of the middle from the sides, several rows of boards were nailed). In 1552, after taking Ivan the Terrible Kazan, and then the conquest of Astrakhan in 1556, these cities become centers for the construction of ships for the Caspian Sea. With Boris Godunov, unsuccessful attempts were undertaken to establish a military fleet in Russia. The first in Russia, the sea ship of the foreign design "Frederic" was built in 1634 in Nizhny Novgorod by Russian masters. In 1667-69, on shipyard in p. Dedinov was built by the eagle sea ship by the organizer of the construction was the boyar Ordin-Nachekin. Further development of the Russian fleet is closely related to the name of Peter the first. And with her and the history of the sail leaves the distant past. So far that it is no longer possible to find out who actually invented the sail. Initially, sails were only an auxiliary vessel of the vessel, but gradually, with the development of sails and improving the ship's shipment, he took the main place, and then completely displaced the propeller propeller (oars). We will consider only ships that are presented in the game "Corsary", that is, the sailboats of the period of the XV - XVIII centuries. But in order to see from where they appear back to come back a little. One of the genericants of the Terrible Sailboats of the XV - XIH centuries is nave. This type of ship was greatly distributed at the end of the XIII century in Europe, although his story dates back to earlier times, approximately the era of the late Roman Empire. There are various interpretations of this word. Most likely it is French origin. Approximately the ship looked like this: length with superstructures about 40 m.; The total height of the housing (from the keel to the upper deck of the add-ons) is about 12 m.; width - 12.5 m; sediment -3.7 m.; Displacement of about 500 tons. The boards were straight, so all the decks had the same width. Two (on both sides) of short with wide blades of cheer, who served as rulings were installed in the stern part of the nef. Two single-trial masts with straight sails were installed on the neopa. Thus was the non-end of the XIII - middle of the XV centuries at the end of XV in the substitution of the same bore nasal nose and the sterns in the nefach appear flat feed tip in the surface part. Instead of steering, the steering wheel was installed, which significantly improved handling and maneuverability. The side, ranging from Waterlinnia, was covered in inside, as a result, the upper deck became almost twice the greatest width of the vessel. This made it difficult to the action of the enemy during Abordage. The ships of this era are long, narrow, with high sides and a small sediment, and, accordingly, with a small margin of stability. The nautical qualities of these ships allowed them mainly in the summer season. The next step in the history of navigation has become Karavella. They are known as the first ships that crossed the Atlantic. Since the XV century, Karavellas were durable, with good nautical qualities of one-lobby courts. They were small (20 - 30 m.), But had 4 masts. A quadranular sail was installed on the front mast, on top of his second, rectangular-marcel. On the other masts was Latin sailing weapons. With such a snap, Karavella could walk with all winds and easily change the course. Karavel speed reached 14-15 knots.
Another characteristic type of ship was a Koraka - a sailing ship who was great fame in the XV - XVI centuries. Presumably the design of the Karakki belongs to the Portuguese, although the ships of such a design were built in Venice. Karakki are also famous by the fact that it is the courts of this type that began to build with large displacement (up to 2 thousand tons). One of these vessels was built in 1592. It had a displacement of 1600 tons, useful carrying capacity of 900 tons, a length of 50 m., Width of 14.3 m., The height of the grotto is 37 m. The ship could take on board up to 700 people. Further development of shipbuilding science led to the creation of Galloon. This name, which originates from the gallers received ships, are longer than no oil and distinguished by the best driving qualities, especially with side winds. Gallows were built with three-family decks received the greatest spread in the Spanish Fleet. One of the Spanish galleons with displacement of 1600 tons, had a length of 54 m., Width of 14.5 m. And the sediment is about 10 m. The high board ended in a large dust in the inside, like non-reserves. As a rule, halons had a high shock, but very low maneuverability and as a result - bad seaworthy qualities. Very widely used Spaniards for transportation between American colonies and metropolis. With the expansion of geographical discoveries and an increase in trade with colonies, there is a need for more speed, maneuverable and reliable ships. At this time, the characteristic previously high superstructures and turrets on the stern and nose are gradually disappeared. The design of the ships, their sailing weapons is improved, maneuverability increases. In the middle of the XVI century, new types of ships are called frigates. Initially, frigates were called any sailing ships, characterized by good nautical qualities. One of the first frigates "Constant Warwik", built in 1646 had a displacement of 315 tons, a length of about 30 m. Then the dimensions of the frigates increased. There was a division into new types of ships: Brig, Brigantine, Schunun, Bark, etc. In the overwhelming majority of cases, the difference was determined by the features of sailing weapons. The frigates became an independent class of ships. Due to the optimal combination of qualities (speed, load capacity, stability, etc.), they quickly won popularity and became the most common type of ships. At the same time, shipbuilders begin to understand that to build a ship that would have excellent combat and trade qualities impossible, and the division of ships for military and trading. The main requirements for the first were maneuverability, speed, strong housing and the number of guns, for the second - the capacity of the trim. The term has appeared - a warship. In essence, it was the same frigate differing from the commercial less than the trumulus and a large number of guns. XVI - XVII centuries. In the ocean expanses, a great many different types of Western European courts were swimming. But the word "type" should not be understood in the current sense.
Ship masters admirated from each other as a separate improvement and the overall layout of the courts, however, their products had only some general signs that justify the use of the unifying name "Type of Ship". Individual performances of even the same type of courts differed in many ways. Almost the only sign by which the ship could be confidently attributed to such a type of sailing weapons. At this time, the features of the national shipbuilding, which most clearly manifested itself in the external outlines of the courts. In general, this period was characterized by several trends in the construction of ships. So the ships of the Dutch building were wider, with a middle height of the side and a smaller sediment than ships of the same type of other countries. The British ships were distinguished by a relatively low side so that in two-candy ships the lower deck was below the Waterlinia and the cannon ports of the lower deck were only 0.5 - 0.6 m. Above water and they had to close with strong excitement. During the English - Dutch war, the Flotovodians used used a new receipt of the battle, when the ships were built into the column column (line) and walked each other in turn shelling target. With this method of conducting a battle, maneuverability went to the second plan and the main one became the number of guns on board. There was a new class - linear ships. The initial linear ships were little, since it was very difficult to build a long durable case, and the amount of guns only increase due to an increase in the number of decks led to a significant decrease in speed and stability. But with the invention of longitudinal screeds, the problem of the strength of the case was solved and the European powers began to quickly build all new and new ships of this class. Introduction 1. Historical shipbuilding development 2. Formation of shipbuilding 3. Sailing fleet and transition to mechanical movement Bibliography Introduction Shipbuilding is one of the most ancient industries. The beginning of it is separated from us a tenth of millennia. The history of shipbuilding begins on the emergence of the first rafts and boats, taken out of the whole wooden trunk, to modern handsome liners and rocket ships, goes to their roots in deep antiquity. It is as multifaceted and has the same age as the history of mankind itself. The main incentive of the emergence of navigation, as well as the shipbuilding associated with him, was the development of trade between peoples, separated by the marine and ocean expanses. The first ships moved with the help of cheerful, only occasionally using as auxiliary force - a sail. Then, approximately in the X - XI centuries, purely sailing vessels appeared along with rowing courts. The shipbuilding industry, being one of the most important sectors of the national economy and possessing scientific and technical and industrial potential, has a decisive influence on many other related industries and the country's economy as a whole, as well as its defense capability and political position in the world. It is the state of shipbuilding that is an indicator of the scientific and technical level of the country and its military-industrial potential, accumulating in its products to achieve metallurgy, mechanical engineering, electronics and new technologies. 1. Historical shipbuilding development From time immemorial, people used water expanses - rivers, lakes, the sea - first as hunting grounds, and then as comfortable roads for moving and transporting goods. The first primitive vessels appeared for a long time to the wheel wagon. The man came out at sea at the dawn of his formation. Mythology Vintage Travel Descriptions and Saga allows you to collect information about the courts. Sometimes they are quite detailed in them to the construction and equipping the "first ships", indicating that they built their people by the will of the gods. This is the case with a noah ark. Oldest Chelny Namerheil from Pessa, Granking (Netherlands), -6315 + 275 BC Already about 2500 years BC. Courts were different: for the carriage of goods, for the transport of passengers. They were driven by poles, oars and sails. In those days, the vessels were mainly military, shopping or fishing. Later appeared vessels for recreation, on which they swam, just for the sake of entertainment. Such a vessel Roman Emperor Caligula (37 - 41 years .: AD) ordered to build for his fishery trips to Lake Nali. An unusually wide and flat design of the vessel is explained by its appointment: a ship for courtiers. The case itself was dialed out of wood, and hollow beams made of burned clay were used as a pitch of the upper deck. To ensure the impermeability and preservation of the vessel, the outer sheat board were covered with lead plates, the inner flooring consisted of marble tiles. In Russia, shipbuilding and navigation were known from the most remote times. Fashionable drawings dating from about 3000 years BC, depicting hunting with harpoon on the marine beast met on the coast of the White Sea. One of the oldest courts found in Russia dating about 5V. BC. In all Slavic languages \u200b\u200bthere is a word ship. His root is "bark" - underlies such words as "basket". The oldest Russian courts were made from flexible rods, as a basket and were trimmed with a bark (later - leather). It is known that already in the 8th century. Our compatriots swam in the Caspian Sea. In the 9th and first half of the 10th century. The Russians were the full owners of the Black Sea, and not in a gift at the time the eastern peoples called him "Russian Sea". At 12 in. For the first time, deck courts were built on Rus. Decks designed to accommodate warriors at the same time served as protecting rowers. Slavs were skilled shipbuilders and built vessels of various designs: Schitik - a flat-bottomed ship with a mounted steering wheel equipped with a mast with direct sail and oars; Carbas - equipped with two masts that carry straight rail or sprinkle sails; Pomeranian Lady - had three masts that were carrying on a straight savory; Rowish is a vessel, where the housing in the underwater part had an ovoid shape. Due to this, when compresseding ice, among which it was swimming, the vessel "squeezed" to the surface, without exposing the deformations and was immersed again in water during the diverge to the ice. The organized maritime shipbuilding in Russia began at the end of the 15th century, when the shipyard was founded in the Solovetsky monastery for the construction of commercial ships. Later already in 16-17 centuries. A step forward was made by Zaporizhzhya Cossacks who committed a raid on the Turks on their "seagulls". The construction technique was the same as in the manufacture of Kiev Nabe Ltodel (in order to increase the size of the vessel to the bottom of the middle from the sides, several rows of boards were nailed). In 1552, after taking Ivan the Terrible Kazan, and then the conquest of Astrakhan in 1556, these cities become centers for the construction of ships for the Caspian Sea. With Boris Godunov, unsuccessful attempts were undertaken to establish a military fleet in Russia. The first in Russia, the sea ship of the foreign design "Frederic" was built in 1634 in Nizhny Novgorod by Russian masters. In 1667-69, on shipyard in p. Dedinov was built by the eagle sea ship by the organizer of the construction was the boyar Ordin-Nachekin. Further development of the Russian fleet is closely related to the name of Peter the first. In June 1693, Peter I laid in Arkhangelsk the first government shipyard for the construction of warships. A year later, Peter visited Arkhangelsk again. By this time, the 24-cannon ship "Apostle Paul", the "Holy Prophecy" frigate, Galen and the Flame transport vessel, formed the first Russian military flotilla on the White Sea. The creation of a regular navy has begun. In the spring of 1700, a 58-cannon ship "Goto Predistinating" was built. In 1702, two frigates were launched in Arkhangelsk: "Holy Spirit" and "Mercury". In 1703, St. Petersburg was laid by the center of which the Admiralty was - the biggest shipbuilding shipyard in the country. The first major vessel who came down from the ADMIRALY shipyard was built by Fedos Sklyaev and Peter the first in 1712, the 54-gun ship "Poltava". By 1714, Russia had its sailing fleet. The biggest ship of Petrovsky was the 90-cannon ship "Forest" (1718). Under Peter I, the following ships were introduced: Ships - 40-55 m long, three-way with 44-90 cannons; Frigates - up to 35 m long, three-way with 28-44 guns; Shnyavi - 25-35 m long, two-dimensional with 10-18 guns; Parma, Ber, Flute, etc. up to 30 m long. In 1719, the serf Efim Nikonov appealed to Peter with a petition about the resolution of the model of the first "hidden" vessel. The first test, held in 1724 ended in failure, and after Peter's death, all work was discontinued. The period of the clutter, experienced by Russian shipbuilders after Peter I was replaced in the second half of the 18th century. new lifting, and by the end of the 18th century. A Black Sea Fleet was created. At the beginning of the 19th century. An technically sound classification of ships was introduced. At the board of Alexander I, shipbuilding works were reduced, but the river shipbuilding continued. It appeared very perfect for his time (Kon. 18 c.) Type of wooden cargo ship - extension. In 1782, the Kulibin Waterselter was built. At the beginning of the 19th century. A successful "car" with the use of horses invented Master Durbaev. The first flight steamer on the St. Petersburg-Kronstadt line was built in 1815. On the reached to us it is clear that the pipe is brick. In a later drawing, the pipe is iron. In 1830, in St. Petersburg, the cargo-passenger vessel "Neva" was lowered, except for two steam vessels also sailing arms. In 1838, in St. Petersburg, there was a test on the Neva The world's first electric power. In 1848, Amosov built the first Archimedian screw frigate in Russia. Especially rapidly began to develop shipping company on the Volga and other rivers after the cancellation of serfdom in 1861, the Sormovsky plant became the main shipbuilding enterprise in 1849. Here were built the first iron barges in Russia and the first commodity-aassay steamer. The world's first use of a diesel engine on river vessels was also carried out in Russia in 1903 In the second half of the 19th century. The iron ships came to replace the iron. It is curious that in Russia, two submarines in 1834 were the first military metal ships in 1834. In 1835, a semi-naval vessel "bravery" was built. It was immersed below the sea level leaving only a smoke pipe over the water. At the beginning of the 19th century. The vessels appeared steam vessels, and the use of first forged iron, and then rolling steel as a structural material during the construction of the vessels led in 1850-60. to the revolution in shipbuilding. The transition to the construction of iron vessels demanded the introduction of a new technological process and the complete transformation of the plants. In 1864, the first armor-floating battery was built in Russia. In 1870, 23 armored ships were already 23 in the Baltic Fleet. In 1872, the carmen "Peter Great" was built - one of the strongest ships in the world for those times. For the Black Sea Fleet A. Popov developed a project of the Barniolesale of Coastal Defense Novgorod in 1871. In 1877, the first torpedo boats in the world were constructed Makarov. In the same year, the first seawater destroyer "Explosion" was lowered. Russian transport shipbuilding of the late 19th century. significantly lagging behind the military. In 1864, the first icebreaker ship "Pailot" was built. In 1899, an icebreaker "Ermak" was built (floating until 1964). 2. Formation of shipbuilding shipbuilding Shipbuilding Fleet Modern historical science does not define any accurate dates about the construction of the first maritime courts, but in all written testimonies that have come down to this day are mentioned about maritime courts and on the existence of maritime trading routes that bind to almost all human civilizations on the world's coast. The chronologically connected history of Mediterranean civilizations in no way denies the developed Eastern maritime infrastructure, since the existence existing in the quiet and Indian Oceans. In the legends and narratives of the ancient Greek philosopher Plato, even about an even more ancient marine civilization - Atlantis, dominious not only on the European and African coasts of the Atlantic, but also on the American continent, and with chronological references 9,000 years BC. Like the amazing historical monuments of terrestrial construction and unique in the technological complexity and beauty of the masterpieces of the city architecture of antiquity, such a perfect sea fleet existed at all times of human civilization and was always the personification of the most advanced scientific thought and the production potential of marine states. Historical certificates of long-range campaigns of the ancient navigators do not allow to reject their ability to determine the location of the vessel away from the shores in clear or cloud weather, during the day or night, as well as their knowledge of marine currents, tides and lowers, the loyalty of weather predictions and sea winds. In addition to purely theoretical navigation and astronomical sciences, geographical knowledge in marine laws and travel manuscripts, the art of navigation requires preservation and transmission from generation to generation of unwritten practical experience, maintaining high centers of sailors who can take confident, accurate and bold shipment solutions on the storm winds of the open Sea and dangerous fairway coastal routes. The ancient indirect certificates about the architectures of ships and the conditions of naochetia often confirm the high marine art of East Asian countries, from where in the Mediterranean, shipbuilding technologies came, new technical means and navigation sciences about far ship shipment. The generally accepted and documented inseparable history of the navigation takes its beginning only from medieval Europe, from the mighty and numerous Venetian fleet. During the crusades (1096-1270), Venice was the main supplier of large vessels. In the following centuries, the design of these vessels was constantly changed, and by the beginning of the XVI century, the Venetian four-volume nave had a completely perfect body shape and significant sizes. Fock and grotto masts carried straight sails, the second grotto and bizan-mast - Latin. Such sailing arms allowed to walk fairly cool to the wind. Until the beginning of the 20th century, each large ship was considered a unique engineering structure, in the design and construction of which the seafarers themselves were direct involved, which had a great experience of marine campaigns and trouble-free shipments in complex and stormy floors. Responsibility for the seaworthy qualities and the safety of navigation of new ships was completely in the same old marine captains, in anticipation of new distant campaigns by coastal shipping, building new ships for their own future campaigns, taking into account both the historical experience of shipping and their own practical skills and knowledge of features The operation of the ship in the ocean swimming. Thus, the continuity of shipbuilding science was rigidly believed to the abilities of the designers - captains, as well as the crews subordinate to them to the fulfillment of long marine expeditions, maintaining the combat capability of the ship and their lives in the harsh conditions of swimming on them of designed ships. It can be taken for the truth statement that if certain design solutions on the shape of the body and ship architecture persisted in centuries and were replicated simultaneously in several countries, then the corresponding ships can be considered quite navigable or optimal in terms of swimming conditions in the specified areas of the ocean or, on the maritime slang satisfying the requirements "Good Marine Practice" (the best and historically verified technical solutions that meet the modern conditions of navigation). Obviously, not the ship that can swim in general is good, but only one that is able to respond to the requirements for autonomy, carrying capacity, movement speed and controllability in simple and complex floors of the navigation. At all times, the person tried to adapt the vessel to the interaction with the surrounding water and the air. Namely to the storm, these two environments are water and air, interacting with each other, generated the most dangerous factors. These are terrible waves under the alarm-hurricane winds. Long-term time experience in the construction of river and maritime courts was acquired by the method of trial and errors, which led to very long historical terms in the evolution of shipbuilding. Often, the experience gained with his carriers - sailors. The followers were forced to repeat their way or create something new in the area of \u200b\u200bshipbuilding and navigation. The first thing they came to the seafarers thinking are: the fight against the swelling elements is absolutely hopeless. Rowers in storm conditions are quite quickly embarrassed out of the forces, and the oars, if they do not remove them, breaks and crippling. The sail breaks, the mast breaks - as a result, an uncontrollable ship with crew, cargo and passengers, who are praying for all known gods about mercy, remain on the surface of the stormy sea. And here, in such an alarming clock, except for prayers and appeals, the true sailors noted that wide and rounded hulls with high cheekbones are able to hold the lag on a large wave, practically not faster, and round, like barrels - less than all the cribs and breaks under the blows of the waves, Even if on the narrated decks, the formidable wave flows are often enveloped. The non-resistance of the storm element, as the main rule of consistent design, is brightly manifested in the form of a body and the generally laborious architecture of all the most famous historical ships and ships of the ocean navigation. The emergence of sailing vessels of an unlimited area of \u200b\u200bswimming led to the era of great geographical discoveries, when the Spanish fleet visited almost all remote areas of the World Ocean for several decades of the late XV centuries. But in the middle of the XVI century, the "invincible Spanish Armada" suffered a crushing defeat from the storm element in swimming around the UK islands, when in the absence of a minimum navigation and hydrographic arrangement of the coast, accurate navigation cards and the necessary knowledge of the hydrometeorological conditions of the diving area, most of the ships of the Great Squadron It turned out to be on the stones and chambers near the coast. And now there are a lot of coastal waters of the World Ocean, unsecured harbors - asylums from storm winds. When swimming in such open waters, ships and ships can only rely on the experience of captains and on their own storm seaworthy qualities. To a certain extent, such dangerous areas include coastal water areas near Sakhalin, Kamchatka and Kuril Islands, where storm seaworthiness is the most important condition for maintaining the effectiveness of marine transport communications and a mandatory requirement for ships and maritime engineering structures involved in the development of marine natural resources. 3. Sailing fleet and transition to mechanical movement Returning to the issues of designing real historical ships, it can be noted that as the principles of bringing the ship in motion, already on galleries and sailing ships (Pallada frigate), there are cases of ensuring storm-sailing regimes due to the active use of storm sails, which allowed several simplified The shape of the housing and the architectural appearance of these ships, as well as to ensure substantially better quality qualities on moderate excitement (Cati-Sark clieper). The Russian fleet was created under the influence of the European shipbuilding school, which by that time reached the level of design of the best sailing vessels on the nautical qualities. The ships of the English architecture of the building were the first Russian ship "Eagle", as well as those built in the Far East Petr and Paul package. The main ships of Peter I belonged to the Dutch ship school, they no longer had a developed forage superstructure and were quite high in the nose. This meant that by analogy with the Baltic countries, the shipbuilding program of Peter I, first of all, took into account the need to provide neighboring marine communications in the Baltic and in the Northern seas. In the XVIII century, sailing arms reaches absolute perfection, now there is no need to solve the task of safe storm swimming only by designing a special form of the body. To confront the storm wielding and the hurricane wind, sailing weapons are actively used. The navigators put the task of maintaining a given course and the maximum speed of the course even in conditions of very fresh winds and moderate storms, in which low-tonnable carriages of the era of great geographical discoveries were necessarily moved to the storm mode without turn. The deck of the sailing ship is hidden and becomes continuous, and sometimes it is almost horizontal, like the Pallada frigate. To improve maneuverability, a variety of spit sailing weapons are now widely used, on the weak winds, the rei-straight sails are led by Lissel alcohols, and the vessel's stormy weather is confidently holding a course with the help of special storm sails, or reefs on the lower sails are used to reduce their area. If the strength of the hurricane exceeds the possibility of the carriage management crew, then the radical emergency remains: "Fock mast - overboard" as a floating anchor, which turns the storming speed sailboat into its historical prototype with sailboat shifted in the stern due to the remaining mast, and The nose, pressed against the strength of the resistance of the towed fock mast. Unfortunately, modern vessels with mechanical engines do not have similar emergency tools, and at the same time exploitation of engines and steering machines in storm conditions is often conducted with serious or even dangerous overloads. The beginning of the XIX century is celebrated by the construction of the first vessels with steam machines. In 1815, the first Russian wheeled steamer, which was called "Stamp" or "Elizabeth," stood on the line Petersburg - Kronstadt. In 1819, the American Wheeled Steamer "Savannah" crossed the Atlantic from New York to Liverpool for 24 days, passing only a small part of the path under the sail. The mechanical drive significantly increases the ship's navigation, which is due to the possibility of maintaining the course of an arbitrary course at any state of excitement. An effective mechanical propulsion is able to overcome the onslaught of the storm element, and with a small steering skill in the dynamics of avaavation between the waves can save any, even the most inconspicuous floating structure. The new engine, being a complex mechanical structure, attracted by the ships of highly qualified specialists - mechanics, which, by virtue of their younger ingenuity, began to bring the psychology of the power "conquest" of the sea on the fleet, instead of the traditional maritime rules of non-resistance of the marine element. But at first, the requirements of the effectiveness and efficiency of navigation rather quickly led to the emergence of new "unwritten" rules for good maritime practice, as in the sailing fleet, compiled using the real experience of stormy navigation. New ocean ships of all countries of the world have quite quickly acquired the same external form, which is a necessary sign of the existence of global optimality criteria in the design of the ship, which also testified also on a unified approach to ensuring the ship's seediness on moderate excitement and in stormy floors. But nevertheless, the first rowing wheels were installed on sailing vessels as an additional propultery, and due to the technical imperfection of the main engines such steamers had all the disadvantages of the most honest vessel: Wide deck; Vulnerability of the propeller - rowing wheels; Difficulties in using rowing wheels on large excitement. The first major vessel "Great Britain", equipped with a propeller, was built in Bristol in 1843. Then for 50 years, the shape of the enclosure of the All-Year Ship undergoes consistent evolutionary changes, which, nevertheless, always and fully inherited the best properties of their sailing and most predecessors. There is no doubt that in the widths of the ship built at the beginning of the 20th century, it is possible to read compromise solutions between humility and confrontation in front of the marine element: Taran-boulevard continues to serve as a means to stabilize the housing and preserve stability in the course in conditions of excitement. Especially important that for high speed, compared with the Gallery on Village, this bouler has favorably affects the decrease in wave resistance also on calm water; The pointedness of the tips and the small fullness of the surface volumes in the nose and in the stern contribute to the attachment on excitement and favorably affect the decrease in the killeep and preventing the heming; The sides of the sides in the middle part of the case prevents concentrated shutting blows on the surface board of the ship, and the Middle-pin round, and in general, the verte-shaped and symmetrical to the central line of the case do not allow strong digging and loss of the course when driving almost any course relative to the storm excitement; Practically, all ships marked the stem cut under water below the Taran, which contributes to stability, on the course with rises on a swing and at the same time allows the corpus to be looser to a slam with large waves and swear; Also, like the Mediterranean gallers, the narrow vehicles enclosures are built to achieve high speed; The narrowed overall width of the deck and long longitudinal superstructures serve the objectives of preserving storm storminess in the conditions of high ventulosity of the upper decks; A fairly low surface board and a small sailness of the add-ons give great opportunities for driving the ship and maneuvering in conditions of strong winds. Many squadron armor, as well as cruisers and destroyers, built at the end of the 19th - early 20th centuries, possessed the ideal architecture of the corps in all these criteria. The linear ships of the first half of the 20th century have no less semi-century, which had understated and pointed tank and the main volume of the housing in them focused in the middle part. This provided a steady motion on the excitement, in which there was no intense killeep, and, accordingly, the possibility of hazardous filliness of the tips was excluded by reducing the total area and continuity of the upper decks of the tank and Utah, as well as the lack of falsebates and the lack of deck bims. Bibliography 1. The history of domestic shipbuilding. In five volumes. Edited by Acad. I.D.Passky. St. Petersburg: "Shipbuilding", 1994. 2. Kurti O. Building vessel models. Encyclopedia of shipyadelism. L.: Shipbuilding, 1977. 3. Mitrofanov V.P., Mitrofanov P.S. Schools under sails. L.: Shipbuilding, 1989. 4. Khmelnov I.N., Tourmov G.P., Illarionov G.Yu. Superwater ships of Russia: history and modernity. Vladivostok: Ussuri, 1996. 5. Polovinkin V.N. History and modernity of domestic shipbuilding. Great people and great things. - Kolomna, 2002. |
Popular:
New
- Hydrogen Communication All Examples
- Barbaric Encyclopedia: Commod, Emperor Lucius Ely Aureli Commoda Mark Azeri Son
- History of creation and development
- History of the emergence of information resources of society
- How the intelligence officer Nikolay Kuznetsov killed (5 photos) Neither Kuznetsov
- Novgorod land (Republic) Culture of Novgorod land in the 12th century
- Poisoning arsenic and its salts - fatal dose for man, symptoms, treatment
- LOST - Railway station overcome whether "Human Factor"
- Essence and principles of collectivization collectivization in the USSR causes essence results
- Socialization hazards. Social hazards. Classification of social hazards. Brief description of the main types of social hazards